ONLINE LEARNING
Call Us
9455049031
Admission-Procedure
TERMS & CONDITIONS
Please read the terms & conditions carefully. Your access to & use of the services is conditioned on your acceptance of & compliance with these terms.
If you disagree with any part of the terms, then you may not access the services.
STUDENT APPLICATION FORM
To apply for any of the course, fill up the Application form available at our offices in your own hand writing or Google form available our website with name of Apply now with Student’s email ID.
The available seats are limited and will be filled in first come first serve basis.
Incomplete Application from will rejected. It is compulsory to attach photocopy of mark sheets and two recent passport size photographs with the enrollment form.
STUDENT REGISTRATION
FORMRegistration Agreement: The “Student Registration Form” is the Registration Agreement (hereinafter referred to as the Agreement) between the applicant and CONCEPT ACADEMY.
It constitutes and expresses the entire agreement and understanding between the CONCEPT ACADEMY and the student in reference to all matters herein referred to, all previous discussions, promises, representations and understandings relative thereto, if any, had between the parties hereto, being herein merged.
After depositing money towards registration, if a student due to any reason whatsoever wants to take his/her money back after the enrollment, the Institute will not refund or adjust the money deposited towards Registration fee/Admission fee.
CONCEPT ACADEMY will be providing all services to Students.
FEE (Terms & Conditions)
Full course fee is mentioned on the form OR discussed before admission, Fee once paid is not refundable under any circumstances. However, the fee may be refunded only if “CONCEPT ACADEMY” fails to start a Course (not applicable for unavoidable instances). Delay in starting of class by a fortnight shall not be considered as not starting.
If any student does not pay the fee on the due date as intimate by SMS or is defaulter in the fee payment, he/she shall be stopped from attending the classes. It is therefore, in the interest of the parents & students that they should deposit the fee on the due dates mentioned.
If student name is struck-off due to non-payment of fee for more than 3 weeks from the due date, the student shall have to pay Rs. 500/- for re-admission.
In case if any parent/guardian misbehaves with any staff member of the CONCEPT ACADEMY, the student can be rusticated from the Institute. The decision of the Director in this regard will be final and binding on the student/parent. No fee or part of the fee will be refunded in such cases.
If any student does not pay the fee on the due date as mentioned in the prospectus or is defaulter in the fee payment, he/she shall be stopped from attending the classes. It is therefore, in the interest of the parents & students that they should deposit the fee on the due dates mentioned.
If student name is struck-off due to non-payment of fee for more than 3 weeks from the due date, the student shall have to pay Rs. 500/- for re-admission.
CONCEPT ACADEMY reserves its right to make any alteration in its programs/venue /timing and days of classes without any prior notice to anybody. The decision of the Director will be final & binding on the students & the parents.
If the teachers feel that the student is not working hard, creating indiscipline in the Institute, irregular in attendance, not responding properly, student may be expelled from the Institute. The decision of the Director in this regard will be final and binding on the student/parent. No fee or part of the fee will be refunded in such cases.
All disputes are subject to jurisdiction of Lucknow High Court branch.
DISCIPLINE
Students are advised-
COMMUNICATION TO THE STUDENTS & PARENTS
In case of any mishap because of reasons beyond control or any natural calamity of any type (earthquake, floods, fire, electric short circuit etc) occurs in the premises of CONCEPT ACADEMY, the institute shall not be responsible in any manner whatsoever
DECLARATION BY THE STUDENT & GUARDIAN
Science is the systematic Knowledge of a particular subjects with causes and effects.
Science is the pursuit and application of knowledge and understanding of the natural and social world following a systematic methodology based on evidence, Experiment and/or observation as benchmarks for testing hypotheses.
PHYSICS
CHEMISTRY
BIOLOGY
MATHEMATICS
ACCOUNTANCY
ECONOMICS
BUSINESS STUDIES
SOCIAL STUDIES
ENGLISH
COMPUTER
26% OFF ON REPUBLIC DAY ADMISSION
REPUBLIC DAY OFFER for Admissions in Classes 7th, 8th, 9th, 10th, 11th and 12th
Syllabus Biology -X
(According to Reduced Syllabus by Board exam 2021)
(FOR CBSE & UP BOARD EXAM 2021)
Life processes: ‘Living Being’. Basic concept of nutrition, respiration, transport and excretion in plants and animals.
Reproduction: Reproduction in animals and plants (asexual and sexual) reproductive healthneed and methods of family planning. Safe sex vs HIV/AIDS. Child bearing and women’s health. Heredity: Heredity; Mendel’s contribution- Laws for inheritance of traits: Sex determination: brief introduction;
Our environment: Eco-system, Environmental problems, Ozone depletion, waste production and their solutions. Biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances.
DOWNLOAD PAPER
ANSWERS
BIOLOGY-X (CBSE & UP BOARD) MS
(B) Pollen grains contain male gametes and ovules contains female gametes in plants.
30. Water re-absorption occurs through villi, undigested food is stored in rectum and thrown out through anus. Exit is regulated by anal sphincter.
31. (A) Heredity (B) Fission.
32. In case of human beings female sex have a pair of chromosomes (sex) and male sex have a pair of XY sex chromosome. When the crossing of male and female gametes takes place then the sex of the child determined as follows:
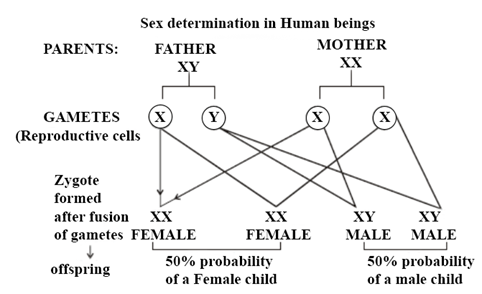
This shows that the ratio of male: female sex of the child is same i.e., (1 : 1), 50% possibility of each is seen here.
OR
1. Guard cells 2. Vacuole 3. Stoma 4. Chloroplast.
33. Seminal vesicles are a pair of thin-walled muscular and elongated sacs which secrete a fluid for nourishment of sperms.
Prostate glands also produce a fluid which is released in the urethra along with secretion of seminal vesicle. It affects the vaginal pH so that sperms move smoothly inside the vagina.
34. In asexual reproduction, the offspring is almost identical to the parent because they have the same gene as their parent. Thus, variation is not present.
Sexual reproduction involves fusion of male and female gametes. The offspring exhibits diversity of characters because they receive some genes from the mother and some from the father. The mixing of genes in different combinations, results in genetic variations. This variation leads to the continuous evolution of various species to produce various organisms.
35.
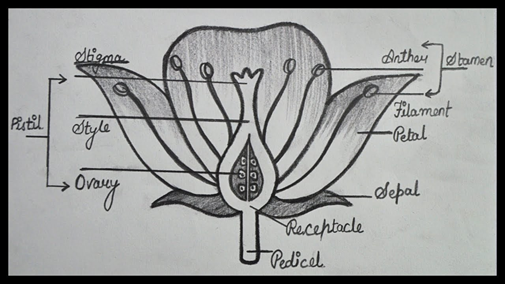
36. The reasons for adopting contraceptive methods could be:
1. Protection from sexually transmitted diseases such as HIV-AIDS, gonorrhoea, syphilis, warts etc.
2. Restricting the number of children.
3. Sufficient gap between successive births.
4. Enjoying a good reproductive health.
5. Controlling population.
37. (i) Water: Roots absorb it from the soil.
(ii) Carbondioxide: Stomata in leaves allow the carbon dioxide gas to enter into the plant.
(iii) Chlorophyll: It is already present in the leaves.
(iv) Sunlight: From the sun.
38.
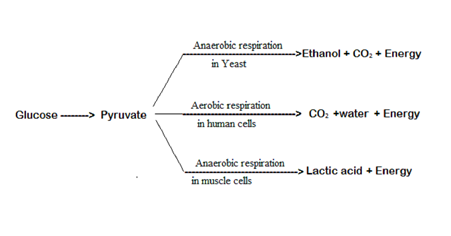
OR
(a). (A) Hydra (B) Rhizopus
(C) Bryophyllum (D) Planaria
(b) Asexual mode of reproduction
(c ) (i) Only one individual is required. (ii) Progeny is identical like parents (iii) Produced in large number (Any two)
39. (a) Rr and Rr.
(b) Red colour of flowers is the dominant trait while white colour is the recessive trait.
(c) Monohybrid cross, phenotypic ratio is 3 : 1.
40.
– Passes through glomerulus in the Bowman’s capsule
–Ultra filtration – Filtrate initially has glucose, amino acids, water, salts and nitrogenous waste – Reabsorption
– Water (as per the need of the body),
Glucose and amino acids are all reabsorbed
– – Secretion of excess water, salts and urea (nitrogenous waste) which makes up the urine
41. (A) Heating of lead nitrate; and electrolysis of acidified water
(B) Oxygen is carried by haemoglobin present in the RBC of the blood, carbon dioxide is soluble in water and hence is transported by the blood in dissolved form.
42.
concave portion faces medially. The kidney collects and transports urine from the kidney to ureters.
The kidneys regulate:
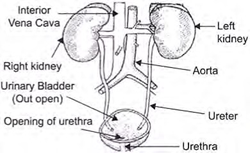
OR
CONCEPT BOOSTER TEST SERIES 2021 BOARD EXAMS
Are You Preparing for CBSE Board Exams 2025?
ACCESS THOUSANDS OF QUESTIONS & MANY TESTS
Benefits of Concept Booster Test Series
Every Year CONCEPT BOOSTER TEST SERIES conducted by Team Concept Academy for Board Exams.
Test Series 10 January – 02 May 2021
BOARD Xth-2021
| SUBJECTS | No. of Tests | Syllabus |
| PHYSICS BOOSTER TEST | 1 | Complete Physics |
| CHEMISTRY BOOSTER TEST | 1 | Complete Chemistry |
| BIOLOGY BOOSTER TEST | 1 | Complete Biology |
| MATHS BOOSTER 1/3 PART TEST | 3 | One Third Part of math’s |
| HISTORY BOOSTER TEST | 1 | Complete History |
| GEOGRAPHY BOOSTER TEST | 1 | Complete Geography |
| CIVICS BOOSTER TEST | 1 | Complete Civics |
| ECONOMICS BOOSTER TEST | 1 | Complete Economics |
| SCIENCE BOOSTER TEST | 4 | Complete Science |
| MATH’S BOOSTER FULL TEST | 4 | Complete Mathematics |
| SST FULL BOOSTER TEST | 3 | Complete Social Science |
| ENGLISH TEST | 2 | Complete English |
| HINDI BOOSTER TEST | 2 | Complete Hindi |
| Total | 25 | Tests |
BOARD XIIth-2021
| SUBJECTS | No. of Tests | Syllabus |
| PHYSICS PARTS BOOSTER TEST | 4 | 4 Chapters in Each Test |
| CHEMISTRY PARTS BOOSTER TEST | 4 | 4 Chapters in Each Test |
| BIOLOGY PARTS BOOSTER TEST | 4 | 4 Chapters in Each Test |
| MATHS PARTS BOOSTER TEST | 4 | 4 Chapters in Each Test |
| PHYSICS FULL BOOSTER TEST | 3 | Complete Syllabus |
| CHEMISTRY FULL BOOSTER TEST | 3 | Complete Syllabus |
| BIOLOGY FULL BOOSTER TEST | 3 | Complete Syllabus |
| MATHS FULL BOOSTER TEST | 3 | Complete Syllabus |
| ENGLISH TEST | 2 | Complete English |
| HINDI BOOSTER TEST | 2 | Complete Hindi |
| Total | 25 | Tests |
(a) Diffusion, evaporation, compression of gases
(b) Evaporation, compression of gases, solubility
(c) Evaporation, diffusion, expansion of gases
(d) Evaporation, solubility, diffusion, compression of gases
2. During summer, water kept in an earthen pot becomes cool because of the
phenomenon of
(a) diffusion
(b) transpiration
(c) osmosis
(d) evaporation
3. In which of the following conditions, the distance between the molecules of
hydrogen gas would increase?
(i) Increasing pressure on hydrogen contained in a closed container
(ii) Some hydrogen gas leaking out of the container
(iii) Increasing the volume of the container of hydrogen gas
(iv) Adding more hydrogen gas to the container without increasing the
volume of the container
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
4. Choose the correct statement of the following
(a) conversion of solid into vapours without passing through the liquid
state is called sublimation.
(b) conversion of vapours into solid without passing through the liquid
state is called vapourisation.
(c) conversion of vapours into solid without passing through the liquid
state is called freezing.
(d) conversion of solid into liquid is called sublimation.
5. On converting 25°C, 38°C and 66°C to Kelvin scale, the correct sequence of temperature will be
(a) 298 K, 311 K and 339 K
(b) 298 K, 300 K and 338 K
(c) 273 K, 278 K and 543 K
(d) 298 K, 310 K and 338 K
6. Which of the following tissues has dead cells?
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Sclerenchyma
(c) Collenchyma
(d) Epithelial tissue
(b) Sclerenchyma is a simple permanent tissue comprising of dead cells. The cells are long and narrow with lignified cell walls. The cells of sclerenchyma are closely packed without any intercellular spaces. Sclerenchyma tissue is present in stems (around the vascular bundles), roots, veins of leaves, hard covering of seeds and nuts etc. Besides, cells of surface layers in stratified epithelium are dead, but this tissue does not has both dead and living cells unlike sclerenchyma.
7. Find out incorrect sentence.
(a) Parenchymatous tissues have intercellular spaces.
(b) Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at corners.
(c) Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues.
(d) Meristematic tissue, in its early stage, lacks vacuoles
(c) Apical and intercalary meristems are not permanent tissues but they are meristematic tissues which remain in continuous state of division. These tissues differentiate to give rise to the permanent tissues.
8. Girth of stem increases due to
(a) apical meristem
(b) lateral meristem
(c) intercalary meristem
(d) vertical meristem.
Solution:
(b) Lateral meristem occurs on the sides almost parallel to the long axis of the root, stem and its branches. It is responsible for an increase in girth of the stem, i.e. secondary growth.
9. Which cell does not have perforated cell wall?
(a) Tracheids
(b) Companion cells
(c) Sieve tubes
(d) Vessels
Solution:
(b) Companion cells are narrow, elongated, thin-walled, living cells. They lie on the sides of the sieve tubes and are closely associated with them through plasmodesmata. Companion cells do not possess perforated cell walls
10. Which muscles act involuntarily?
(i) Striated muscles
(ii) Smooth muscles
(iii) Cardiac muscles
(iv) Skeletal muslces
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Solution:
(b) The muscles which are not under the control of our will, are called involuntary muscles. Smooth (unstriated) muscles and cardiac muscles are involuntary muscles.
11. A body is thrown vertically upward with velocity u, the greatest height h to which it will rise is,
(a) u/g (b) u2/2g (c) u2/g (d) u/2g
12. From the given v – t graph it can be inferred that the object is
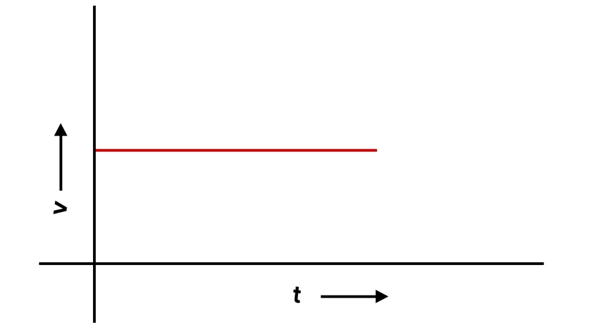
(a) in uniform motion
(b) at rest
(c) in non-uniform motion
(d) moving with uniform acceleration
(Incomplete question in test on 01.09.2024)
13. Area under a v – t graph represents a physical quantity which has the unit
(a) m2
(b) m
(c) m3
(d) m s-1
14. Four cars A, B, C and D are moving on a levelled road. Their distance versus time graphs are shown in figure. Choose the correct statement
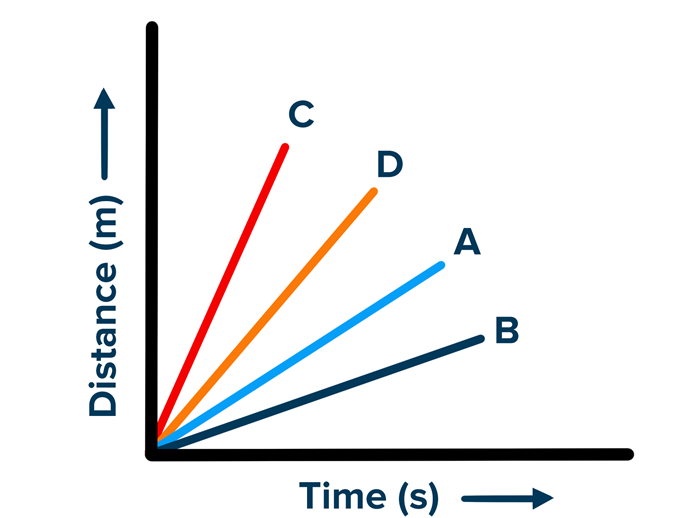
(a) Car A is faster than car D.
(b) Car B is the slowest.
(c) Car B is faster than car C.
(d) Car C is the slowest.
15. Which of the following figures represents uniform motion of a moving object correctly?
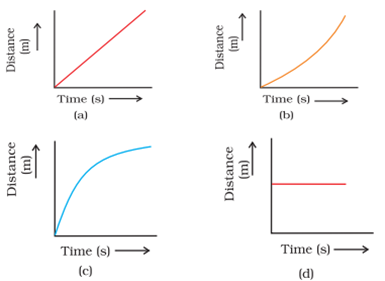
16. Fill in the blanks: (5 Marks)
(a) Evaporation of a liquid at room temperature leads to a ______ effect.
(b) At room temperature the forces of attraction between the particles of solid substances are ______ than those which exist in the gaseous state.
(c) The arrangement of particles is less ordered in the ______ state. However, there is no order in the state.
(d) ______ is the change of gaseous state directly to solid state without going through the ______ state.
(e) The phenomenon of change of a liquid into the gaseous state at any temperature below its boiling point is called ______.
Solution:
(a) Cooling
(b) Stronger
(c) Liquid, gaseous
(d) Sublimation, liquid
(e) Evaporation
OR
Classify the following into osmosis/diffusion:
(a) Swelling up of a raisin 9n keeping in water.
(b) Spreading of virus on sneezing.
(c) Earthworm dying on coming in contact with common salt.
(d) Shrinking of grapes kept in thick sugar syrup.
(e) Preserving pickles in salt.
(f) Spreading of smell of cake being baked throughout the house
(g) Aquatic animals using oxygen dissolved in water during respiration.
Solution:
(a) Osmosis
(b) Diffusion
(c) Osmosis
(d) Osmosis
(e) Osmosis
(f) Diffusion
(g) Diffusion
17. Water as ice has a cooling effect, whereas water as steam may cause severe burns. Explain these observations. (2 Marks)
Solution:
Water in the form of ice has low energy since water freezes at a lower temperature. When ice comes in contact with body it draws heat from the body and gives cooling effect. In case of steam, the water molecules have high energy. The high energy of steam is transformed as heat and may cause severe burns.
18. Alka was making tea in a kettle. Suddenly she felt intense heat from the puff of steam gushing out of the spout of the kettle. She wondered whether the temperature of the steam was higher than that of the water boiling in the kettle. Comment. (2 Marks)
Solution:
The temperature of both boiling water and steam is 100°C but steam has more energy because of latent heat of vaporisation. Hence, steam is hotter than boiling water.
OR
Tabulate the differences in the characterisitcs of states of matter.
19. You want to wear your favourite shirt to a party, but the problem is that it is still wet after a wash. What steps would you take to dry it faster? (3 Marks)
Solution:
The process of drying the shirt can be made faster in the following ways :
(a) Spread the shirt to increase the surface area which will increase rate of evaporation.
(b) Put it in the sun to increase the temperature to increase the rate of evaporation.
(c) Keep it under the fan to increase the wind speed which increases the rate of evaporation.
OR
Convert the following temperature to Fahrenheit scale: a. 3000 C b. 5730 c. -400C
20. Comment any 4 of the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy and density (4 Marks)
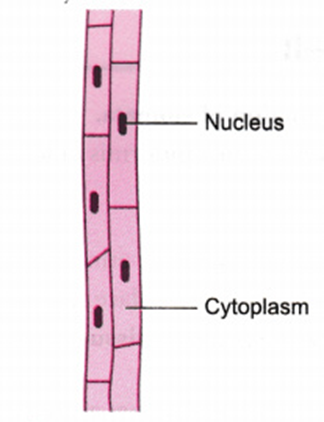
21. Name the different components of xylem and draw a living component.
(4 Marks)
Solution:
Different components of xylem are tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres. Xylem parenchyma is the only living component of xylem whose diagram is drawn below:
22. Write true (T) or false (F). (5 Marks)
(a) Epithelial tissue is protective tissue in animal body.
(b) The lining of blood vessels, lung alveoli and kidney tubules are all made up of epithelial tissue.
(c) Epithelial cells have a lot of intercellular spaces.
(d) Epithelial layer is permeable layer.
(e) Epithelial layer does not allow regulation of materials between body and external environment.
Solution:
(a) T
(b) T
(c) F – Epithelial cells have almost no intercellular spaces.
(d) T
(e) F – Due to its permeability, epithelial layer plays an important role in regulating exchange of materials between body and external environment.
23. Which structure protects the plant body against the invasion of parasites? (3 Marks)
Solution:
Epidermis is a layer of parenchymatous cells that forms the outermost covering of plant body. Epidermis consists of compactly arranged cells without any intercellular spaces. On the aerial plant parts, it secretes a thick, waxy, water-resistant layer called cuticle on its outer surface. These features .make the epidermis protective against loss of water, mechanical injury and the invasion of parasites.
24. Fill in the blanks. (3 Marks)
(a) Cork cells possess _____ on their walls that makes them impervious to gases and water.
(b) _____ have tubular cells with perforated walls and are living in nature.
(c) Bone possesses a hard matrix composed of _____and _____.
Solution:
(a) suberin
(b) Sieve tubes
(c) inorganic, organic substances
OR
List the characteristics of cork. How are they formed? Mention their role.
Solution:
Cork covers the old stems of woody trees. Characteristics of cork are as follows:
Cells of cork are dead at maturity.
These cells are compactly arranged.
Cells do not possess intercellular spaces.
Cells possess a chemical substance suberin in their walls.
They are several layers thick.
Cork is impervious to gases and water.
As plants grow older, a strip of secondary lateral meristem (called cork cambium) develops in the cortical region. It cuts cells towards both outer and inner sides. Gradually, this secondary tissue replaces the epidermal layer of the stem. This forms the several layer thick cork.
Role of cork is as follows:
It protects the internal tissues from mechanical injury and from parasitic attack.
It contains small pores (called lenticels) for gaseous exchange.
It provides mechanical strength.
25. What are the basic difference between xylem & phloem? (2 Marks)
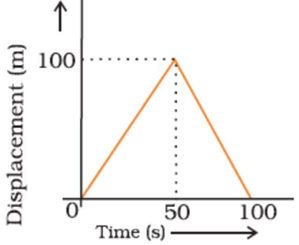
26. A girl walks along a straight path to drop a letter in the letterbox and comes back to her initial position. Her displacement-time graph is shown in figure. Plot a velocity-time graph for the same (2 Marks)
27. A car starts from rest and moves along the x-axis with constant acceleration 5 m s-2 for 8 seconds. If it then continues with constant velocity, what distance will the car cover in 12 seconds since it started from the rest? (4 Marks)
28. A motorcyclist drives from A to B with a uniform speed of 30 km h-1 and returns back with a speed of 20 km h-1. Find its average speed. (3 Marks)

29. The velocity-time graph shows the motion of a cyclist. Find
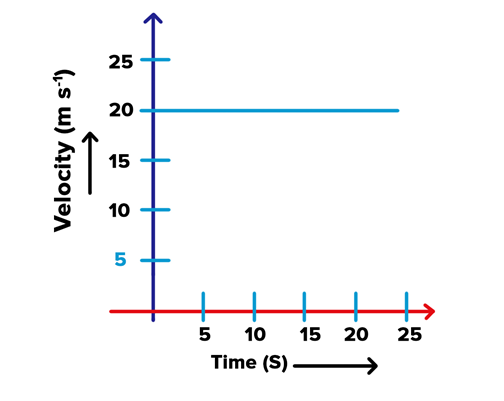
Solution:
Velocity-time graph is a straight line parallel to time axis, so, velocity of the cyclist is constant.
(i) Acceleration = 0
(ii) At, f = 15 s velocity = 20 m s’1 (from the given graph)
(iii) Distance covered by the cyclist in 15 s
= Area under v-t graph during that time interval
= 20 m s’1 x 15 s = 300 m.
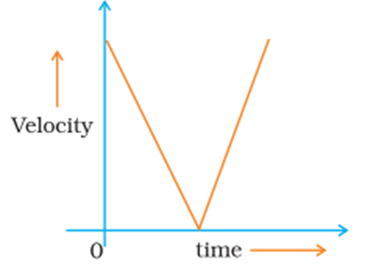
30. Draw a velocity versus time graph of a stone thrown vertically upwards and then coming downwards after attaining the maximum height. (2 Marks)
31. An object starting from rest travels 20m in first 2 s and 160m in next 4 s. What will be the velocity after 7 s from the start. (3 Marks)