- Which one of the following sets of phenomena would increase on raising the temperature?
(a) Diffusion, evaporation, compression of gases
(b) Evaporation, compression of gases, solubility
(c) Evaporation, diffusion, expansion of gases
(d) Evaporation, solubility, diffusion, compression of gases
2. During summer, water kept in an earthen pot becomes cool because of the
phenomenon of
(a) diffusion
(b) transpiration
(c) osmosis
(d) evaporation
3. In which of the following conditions, the distance between the molecules of
hydrogen gas would increase?
(i) Increasing pressure on hydrogen contained in a closed container
(ii) Some hydrogen gas leaking out of the container
(iii) Increasing the volume of the container of hydrogen gas
(iv) Adding more hydrogen gas to the container without increasing the
volume of the container
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
4. Choose the correct statement of the following
(a) conversion of solid into vapours without passing through the liquid
state is called sublimation.
(b) conversion of vapours into solid without passing through the liquid
state is called vapourisation.
(c) conversion of vapours into solid without passing through the liquid
state is called freezing.
(d) conversion of solid into liquid is called sublimation.
5. On converting 25°C, 38°C and 66°C to Kelvin scale, the correct sequence of temperature will be
(a) 298 K, 311 K and 339 K
(b) 298 K, 300 K and 338 K
(c) 273 K, 278 K and 543 K
(d) 298 K, 310 K and 338 K
6. Which of the following tissues has dead cells?
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Sclerenchyma
(c) Collenchyma
(d) Epithelial tissue
(b) Sclerenchyma is a simple permanent tissue comprising of dead cells. The cells are long and narrow with lignified cell walls. The cells of sclerenchyma are closely packed without any intercellular spaces. Sclerenchyma tissue is present in stems (around the vascular bundles), roots, veins of leaves, hard covering of seeds and nuts etc. Besides, cells of surface layers in stratified epithelium are dead, but this tissue does not has both dead and living cells unlike sclerenchyma.
7. Find out incorrect sentence.
(a) Parenchymatous tissues have intercellular spaces.
(b) Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at corners.
(c) Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues.
(d) Meristematic tissue, in its early stage, lacks vacuoles
(c) Apical and intercalary meristems are not permanent tissues but they are meristematic tissues which remain in continuous state of division. These tissues differentiate to give rise to the permanent tissues.
8. Girth of stem increases due to
(a) apical meristem
(b) lateral meristem
(c) intercalary meristem
(d) vertical meristem.
Solution:
(b) Lateral meristem occurs on the sides almost parallel to the long axis of the root, stem and its branches. It is responsible for an increase in girth of the stem, i.e. secondary growth.
9. Which cell does not have perforated cell wall?
(a) Tracheids
(b) Companion cells
(c) Sieve tubes
(d) Vessels
Solution:
(b) Companion cells are narrow, elongated, thin-walled, living cells. They lie on the sides of the sieve tubes and are closely associated with them through plasmodesmata. Companion cells do not possess perforated cell walls
10. Which muscles act involuntarily?
(i) Striated muscles
(ii) Smooth muscles
(iii) Cardiac muscles
(iv) Skeletal muslces
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Solution:
(b) The muscles which are not under the control of our will, are called involuntary muscles. Smooth (unstriated) muscles and cardiac muscles are involuntary muscles.
11. A body is thrown vertically upward with velocity u, the greatest height h to which it will rise is,
(a) u/g (b) u2/2g (c) u2/g (d) u/2g
12. From the given v – t graph it can be inferred that the object is
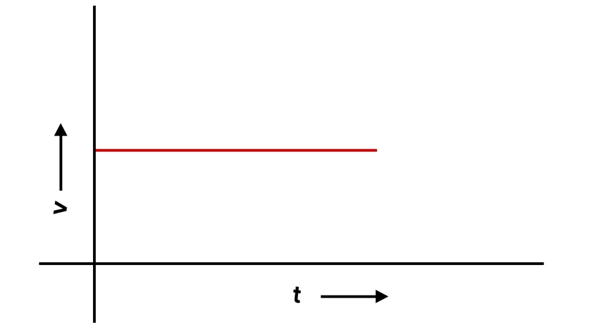
(a) in uniform motion
(b) at rest
(c) in non-uniform motion
(d) moving with uniform acceleration
(Incomplete question in test on 01.09.2024)
13. Area under a v – t graph represents a physical quantity which has the unit
(a) m2
(b) m
(c) m3
(d) m s-1
14. Four cars A, B, C and D are moving on a levelled road. Their distance versus time graphs are shown in figure. Choose the correct statement
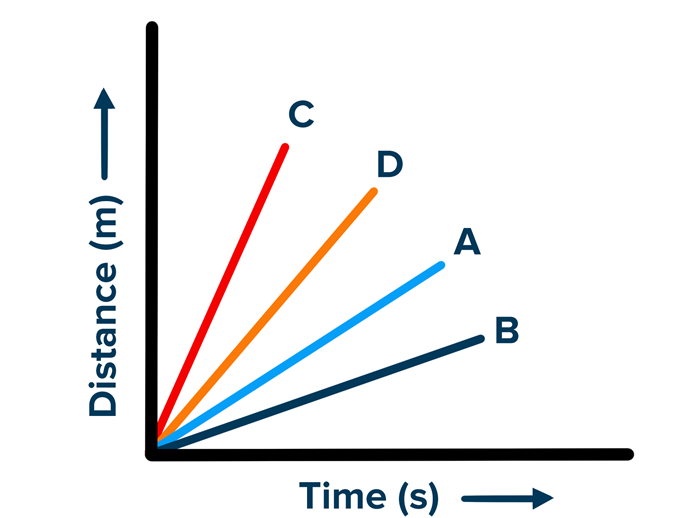
(a) Car A is faster than car D.
(b) Car B is the slowest.
(c) Car B is faster than car C.
(d) Car C is the slowest.
15. Which of the following figures represents uniform motion of a moving object correctly?
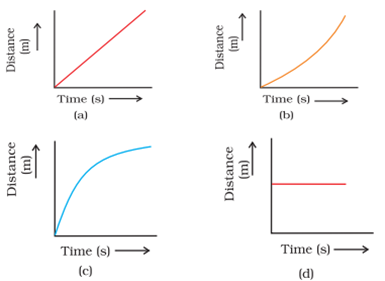
16. Fill in the blanks: (5 Marks)
(a) Evaporation of a liquid at room temperature leads to a ______ effect.
(b) At room temperature the forces of attraction between the particles of solid substances are ______ than those which exist in the gaseous state.
(c) The arrangement of particles is less ordered in the ______ state. However, there is no order in the state.
(d) ______ is the change of gaseous state directly to solid state without going through the ______ state.
(e) The phenomenon of change of a liquid into the gaseous state at any temperature below its boiling point is called ______.
Solution:
(a) Cooling
(b) Stronger
(c) Liquid, gaseous
(d) Sublimation, liquid
(e) Evaporation
OR
Classify the following into osmosis/diffusion:
(a) Swelling up of a raisin 9n keeping in water.
(b) Spreading of virus on sneezing.
(c) Earthworm dying on coming in contact with common salt.
(d) Shrinking of grapes kept in thick sugar syrup.
(e) Preserving pickles in salt.
(f) Spreading of smell of cake being baked throughout the house
(g) Aquatic animals using oxygen dissolved in water during respiration.
Solution:
(a) Osmosis
(b) Diffusion
(c) Osmosis
(d) Osmosis
(e) Osmosis
(f) Diffusion
(g) Diffusion
17. Water as ice has a cooling effect, whereas water as steam may cause severe burns. Explain these observations. (2 Marks)
Solution:
Water in the form of ice has low energy since water freezes at a lower temperature. When ice comes in contact with body it draws heat from the body and gives cooling effect. In case of steam, the water molecules have high energy. The high energy of steam is transformed as heat and may cause severe burns.
18. Alka was making tea in a kettle. Suddenly she felt intense heat from the puff of steam gushing out of the spout of the kettle. She wondered whether the temperature of the steam was higher than that of the water boiling in the kettle. Comment. (2 Marks)
Solution:
The temperature of both boiling water and steam is 100°C but steam has more energy because of latent heat of vaporisation. Hence, steam is hotter than boiling water.
OR
Tabulate the differences in the characterisitcs of states of matter.
19. You want to wear your favourite shirt to a party, but the problem is that it is still wet after a wash. What steps would you take to dry it faster? (3 Marks)
Solution:
The process of drying the shirt can be made faster in the following ways :
(a) Spread the shirt to increase the surface area which will increase rate of evaporation.
(b) Put it in the sun to increase the temperature to increase the rate of evaporation.
(c) Keep it under the fan to increase the wind speed which increases the rate of evaporation.
OR
Convert the following temperature to Fahrenheit scale: a. 3000 C b. 5730 c. -400C
20. Comment any 4 of the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy and density (4 Marks)
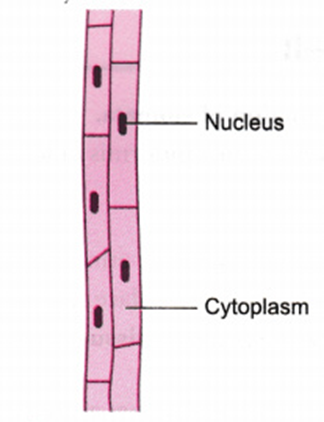
21. Name the different components of xylem and draw a living component.
(4 Marks)
Solution:
Different components of xylem are tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres. Xylem parenchyma is the only living component of xylem whose diagram is drawn below:
22. Write true (T) or false (F). (5 Marks)
(a) Epithelial tissue is protective tissue in animal body.
(b) The lining of blood vessels, lung alveoli and kidney tubules are all made up of epithelial tissue.
(c) Epithelial cells have a lot of intercellular spaces.
(d) Epithelial layer is permeable layer.
(e) Epithelial layer does not allow regulation of materials between body and external environment.
Solution:
(a) T
(b) T
(c) F – Epithelial cells have almost no intercellular spaces.
(d) T
(e) F – Due to its permeability, epithelial layer plays an important role in regulating exchange of materials between body and external environment.
23. Which structure protects the plant body against the invasion of parasites? (3 Marks)
Solution:
Epidermis is a layer of parenchymatous cells that forms the outermost covering of plant body. Epidermis consists of compactly arranged cells without any intercellular spaces. On the aerial plant parts, it secretes a thick, waxy, water-resistant layer called cuticle on its outer surface. These features .make the epidermis protective against loss of water, mechanical injury and the invasion of parasites.
24. Fill in the blanks. (3 Marks)
(a) Cork cells possess _____ on their walls that makes them impervious to gases and water.
(b) _____ have tubular cells with perforated walls and are living in nature.
(c) Bone possesses a hard matrix composed of _____and _____.
Solution:
(a) suberin
(b) Sieve tubes
(c) inorganic, organic substances
OR
List the characteristics of cork. How are they formed? Mention their role.
Solution:
Cork covers the old stems of woody trees. Characteristics of cork are as follows:
Cells of cork are dead at maturity.
These cells are compactly arranged.
Cells do not possess intercellular spaces.
Cells possess a chemical substance suberin in their walls.
They are several layers thick.
Cork is impervious to gases and water.
As plants grow older, a strip of secondary lateral meristem (called cork cambium) develops in the cortical region. It cuts cells towards both outer and inner sides. Gradually, this secondary tissue replaces the epidermal layer of the stem. This forms the several layer thick cork.
Role of cork is as follows:
It protects the internal tissues from mechanical injury and from parasitic attack.
It contains small pores (called lenticels) for gaseous exchange.
It provides mechanical strength.
25. What are the basic difference between xylem & phloem? (2 Marks)
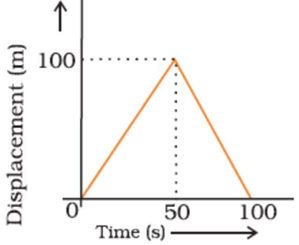
26. A girl walks along a straight path to drop a letter in the letterbox and comes back to her initial position. Her displacement-time graph is shown in figure. Plot a velocity-time graph for the same (2 Marks)
27. A car starts from rest and moves along the x-axis with constant acceleration 5 m s-2 for 8 seconds. If it then continues with constant velocity, what distance will the car cover in 12 seconds since it started from the rest? (4 Marks)
28. A motorcyclist drives from A to B with a uniform speed of 30 km h-1 and returns back with a speed of 20 km h-1. Find its average speed. (3 Marks)

29. The velocity-time graph shows the motion of a cyclist. Find
- its acceleration
- its velocity and
- the distance covered by the cyclist in 15 seconds (3 Marks)
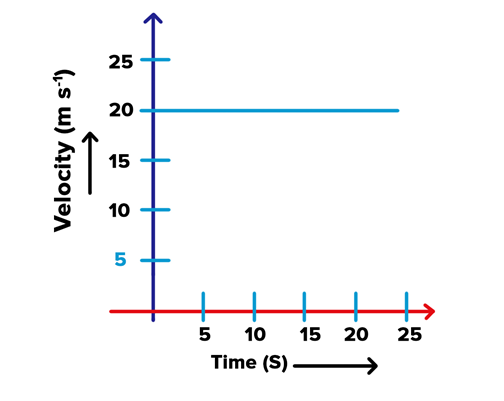
Solution:
Velocity-time graph is a straight line parallel to time axis, so, velocity of the cyclist is constant.
(i) Acceleration = 0
(ii) At, f = 15 s velocity = 20 m s’1 (from the given graph)
(iii) Distance covered by the cyclist in 15 s
= Area under v-t graph during that time interval
= 20 m s’1 x 15 s = 300 m.
30. Draw a velocity versus time graph of a stone thrown vertically upwards and then coming downwards after attaining the maximum height. (2 Marks)
31. An object starting from rest travels 20m in first 2 s and 160m in next 4 s. What will be the velocity after 7 s from the start. (3 Marks)
