Syllabus Biology -X
(According to Reduced Syllabus by Board exam 2021)
(FOR CBSE & UP BOARD EXAM 2021)
Life processes: ‘Living Being’. Basic concept of nutrition, respiration, transport and excretion in plants and animals.
Reproduction: Reproduction in animals and plants (asexual and sexual) reproductive healthneed and methods of family planning. Safe sex vs HIV/AIDS. Child bearing and women’s health. Heredity: Heredity; Mendel’s contribution- Laws for inheritance of traits: Sex determination: brief introduction;
Our environment: Eco-system, Environmental problems, Ozone depletion, waste production and their solutions. Biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances.
DOWNLOAD PAPER
ANSWERS
BIOLOGY-X (CBSE & UP BOARD) MS
- Veins have thin walls because the blood there is no longer under pressure and they have valves to ensure blood flow in one direction
- Fragmentation. Asexual
- The inner lining of the small intestine has numerous finger-like projections called villi which increase the surface area for absorption
- Goat because herbivores eating grass need a longer small intestine to allow the cellulose to be digested..
- The pancreas secretes digestive juice which contains enzymes like trypsin for digesting proteins and lipase for breakdown of emulsified fats.
- b) Both Assertion & Reasoning are correct, Reason is not correct explanation of Assertion
- b) Both Assertion & Reasoning are correct, Reason is not correct explanation of Assertion
- ATP, Adenosine Tri Phosphate.
- Transport of food from leaves to other parts of the plant is called translocation.
- Fungi – saprophytic, Amoeba — animal like nutrition
- Crotons, money plant.
- 23 pairs.
- The trait which represents the tallness in a pea plant is dominant over the another trait, shortness (dwarf).
- Garden pea (Pisum sativum).
- (b)
- (d)
- (a)
- (d)
- (d)
- (a)
- (b)
- (b)
- (b)
- (b)
- (c)
- Trait B is likely to have arisen earlier as it occurs in more number.
- (c )
- Respiratory pigment, haemoglobin is present in red blood cells. Haemoglobin has affinity for O2 thus helping in its transport
- (A) Vegetative propagation can be practised for growing such plants which usually do not produce seeds or produce non-viable seeds.
(B) Pollen grains contain male gametes and ovules contains female gametes in plants.
30. Water re-absorption occurs through villi, undigested food is stored in rectum and thrown out through anus. Exit is regulated by anal sphincter.
31. (A) Heredity (B) Fission.
32. In case of human beings female sex have a pair of chromosomes (sex) and male sex have a pair of XY sex chromosome. When the crossing of male and female gametes takes place then the sex of the child determined as follows:
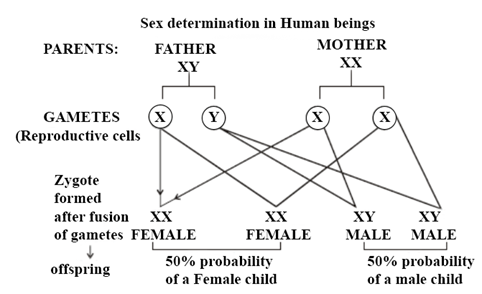
This shows that the ratio of male: female sex of the child is same i.e., (1 : 1), 50% possibility of each is seen here.
OR
1. Guard cells 2. Vacuole 3. Stoma 4. Chloroplast.
33. Seminal vesicles are a pair of thin-walled muscular and elongated sacs which secrete a fluid for nourishment of sperms.
Prostate glands also produce a fluid which is released in the urethra along with secretion of seminal vesicle. It affects the vaginal pH so that sperms move smoothly inside the vagina.
34. In asexual reproduction, the offspring is almost identical to the parent because they have the same gene as their parent. Thus, variation is not present.
Sexual reproduction involves fusion of male and female gametes. The offspring exhibits diversity of characters because they receive some genes from the mother and some from the father. The mixing of genes in different combinations, results in genetic variations. This variation leads to the continuous evolution of various species to produce various organisms.
35.
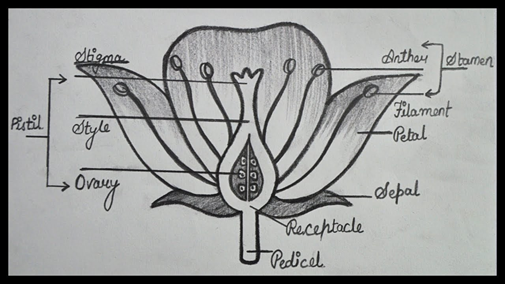
36. The reasons for adopting contraceptive methods could be:
1. Protection from sexually transmitted diseases such as HIV-AIDS, gonorrhoea, syphilis, warts etc.
2. Restricting the number of children.
3. Sufficient gap between successive births.
4. Enjoying a good reproductive health.
5. Controlling population.
37. (i) Water: Roots absorb it from the soil.
(ii) Carbondioxide: Stomata in leaves allow the carbon dioxide gas to enter into the plant.
(iii) Chlorophyll: It is already present in the leaves.
(iv) Sunlight: From the sun.
38.
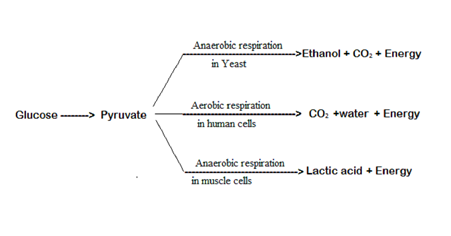
OR
(a). (A) Hydra (B) Rhizopus
(C) Bryophyllum (D) Planaria
(b) Asexual mode of reproduction
(c ) (i) Only one individual is required. (ii) Progeny is identical like parents (iii) Produced in large number (Any two)
39. (a) Rr and Rr.
(b) Red colour of flowers is the dominant trait while white colour is the recessive trait.
(c) Monohybrid cross, phenotypic ratio is 3 : 1.
40.
- Blood passes through filtration units in the kidney called nephron
– Passes through glomerulus in the Bowman’s capsule
–Ultra filtration – Filtrate initially has glucose, amino acids, water, salts and nitrogenous waste – Reabsorption
– Water (as per the need of the body),
Glucose and amino acids are all reabsorbed
– – Secretion of excess water, salts and urea (nitrogenous waste) which makes up the urine
41. (A) Heating of lead nitrate; and electrolysis of acidified water
(B) Oxygen is carried by haemoglobin present in the RBC of the blood, carbon dioxide is soluble in water and hence is transported by the blood in dissolved form.
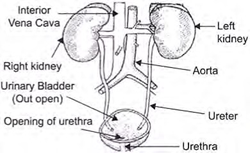
42.
- The kidneys (renal glands) like high in the abdominal cavity near and on both sides of the vertebral column. The right kidney is slightly lower than the left to make room for the liver. Each kidney is bean shaped and the
concave portion faces medially. The kidney collects and transports urine from the kidney to ureters.
The kidneys regulate:
- The volume of blood plasma (blood pressure).
- The concentration of waste products in the blood (excretion).
- The concentration of electrolytes such as Na+, K+, HCO3- and other ions (osmoregulation).
- The pH of plasma.
OR
- The fusion of male gamete with female gamete is known as fertilization.
- Menstruation cycle takes place every month when egg is not fertilized. It lasts for about two to eight days and during this cycle the lining of uterus slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucus.
- Binary fission is the splitting of nucleus into two daughter cells which can take place in any plane. It can be observed in Amoeba.
- When vegetative part of a plant like the root, stem or leaves develops into new plant under appropriate conditions, it is known as vegetative propagation.
- When body of an organism cuts into any number of pieces and each piece grows into a complete organism. This is known as regeneration. Hydra and Planaria reproduce through this process.


5q28es