The Male Reproductive System
1. The testes are situated outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called
(A) urethra (B) scrotum (C)penis (D)none of these
2. In humans, sperms are produced in [Pg-43,E]
(A) epididymis (B) rete testis (C) seminiferous tubules (D) vas deferens
3. Sertoli cells which line the seminiferous tubules from inside [Pg-43,E]
(A) undergo meiotic division to produce sperms (B) provide nutrition to the germ cells
(C) synthesise and secrete testicular hormones (D) All of these
4. Refer to the given figure showing sectional view of seminiferous tubule. In
the figure, some parts are labelled as A, B, C and D. Identify the part which
provides nutrition to the developing sperms. [Pg-44,E]
The regions outside the seminiferous tubules that contain Leydig cells are called [Pg-43,E]
(A) interstitial spaces (B) antrum (C) scrotum (D) none of these
6. Testicular hormones called androgens are secreted by [Pg-43,E]
(A) interstitial cells (B) Leydig cells (C) Sertoli cells (D) both (a) and (b)
7. Which one is odd from the following structures with reference to the male reproductive system. [NCERT Exemplar] [Pg-43,M]
(A) Rete testis (B) Epididymis (C) Vasa efferentia (D) Isthmus
8. The vas deferens opens into urethra as [NCERT Exemplar] [Pg-43,E]
(A) epididymis (B) ejaculatory duct (C) efferent ductile (D) ureter
9. Which of the following depicts the correct pathway of transport of sperms?
[Pg-43,M](A) Rete testis → Efferent ductules →Epididymis → Vas deference
(B) Rete testis → Epididymis → Efferent ductules → Vas deference
(C) Rete testis → Vas deference →Efferent ductules → Epididymis
(D) Efferent ductules → Rete testis → Vas deference → Epididymis
10. Among the following which one is not an accessory duct of male reproductive
system? [Pg-43,E]
(A) Rete testis (B)Vasa efferentia (C) Vas deferens (D)Urethra
11. The ejaculatory duct transports the sperms to the outside through [Pg-43,E]
(A) urethra (B) rete testis (C) vasa efferentia (D) none of these
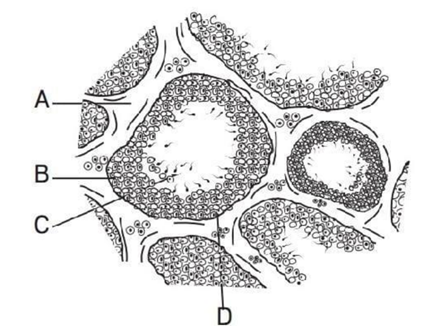
12. Refer to the given figure and choose the correct option for the parts labelled as A,
B, C and D. [Pg-43,M]
a b c d A Vas deferens Seminal vesicle Prostate gland Bulbourethral gland B Vasa efferentia Prostate gland Seminal vesicle Bulbourethral gland C Prostate gland Seminal vesicle Bulbourethral gland Vas deferens D Bulbourethral gland Vas deferens Prostate gland Vasa efferentia
Match the parts given in Column-I to their characteristic features in Column-II and choose the correct option from the codes given below
Column I Column II
(a) Penis (1) Loose fold of skin
(b) Glans penis (2) Male external genitalia
(c) Foreskin (3) External opening urethra
(d) Urethral meatus (4) Enlarged end of penis
a b c d
(A) 2 4 1 3
(B) 3 4 1 2
(C) 2 4 3 1
(D) 4 3 2 1
14. Urethral meatus is/are [NCERT Exemplar] [Pg-43,M]
(A) the urinogenital duct (B) opening of vas deferens into urethra
(C) external opening of the urinogenital duct (D) muscles surrounding the urinogenital duct
15. Among the following which one is not a male accessory gland? [NCERT Exemplar] [Pg-43,E]
(A) Seminal vesicle (B) Ampulla (C) Prostate (D) Bulbourethral gland
16. Match the Column-I (parts) to Column-II (feature) and choose the correct option
from the codes given below. [Pg-43,M]
Column I Column II
(a) Sertoli cells (1) Testicular hormones
(b) Leydig cells (2) External opening of urethra
(c) Epididymis (3) Nutrition to the germ cells
(d) Urethral meatus (4) Male sex accessory duct
a b c d
(A) 4 3 2 1
(B) 3 1 4 2
(C) 1 2 3 4
(D) 2 4 1 3
17. 17. Seminal plasma is contributed by: [NCERT Exemplar] [Pg-44,E]
(I) Seminal vesicle (II) Prostate (III) Urethra (IV) Bulbourethral gland
(A) I and II (B) I, II and IV (C) II, III and IV (D) I and IV
18. Read the following statements about seminal plasma and choose the correct
statement(s) from the given options. [Pg-44,M]
(I) Seminal plasma is secreted by seminal vesicles, prostate and bulbourethral glands.
(II) It is rich in sucrose and calcium.
(III) It contains certain enzymes also.
(A) I and II (B) II and III (C) I and III (D) All of these
19. Read the following statements about male reproductive system and choose the
incorrect statements from the given options. [Pg-43,M]
(I) It is located in the pelvis region.
(II) The testes are situated outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called scrotum.
(III) Each testis has about 350 testicular tubules.
(IV) Penis, the male external genitalia is made up of special tissues to facilitate insemination.
(A) I and III (B) III and IV (C) I and IV (D) Only III
20. Assertion: The scrotum helps in maintaining the low temperature of the testes.
Reason: The low temperature of the testes is necessary for spermatogenesis. [Pg-43,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false.
21. Assertion: The enlarged part of penis is called glans penis.
Reason: The glans penis is covered by a loose fold of skin called foreskin. [Pg-44,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false.
The Female Reproductive System
22. The primary female sex organ is/are [Pg-44,E]
(A) vagina (B) uterus (C) ovaries (D) external genitalia
23. Among the following which one is not the part of female reproductive system? [Pg-44,E]
(A) Cervix (B) Sertoli cells (C)Mammary glands (D) Oviducts
24. The parts that constitute the female accessory ducts include [Pg-45,E]
(A) Fallopian ducts (B) vagina (C)ovaries (D)both (a) and (b)
25. The funnel-shaped part of Fallopian tube that remains closer to the ovary is [Pg-45,E]
(A) infundibulum (B) fimbriae (C) ampulla (D) isthmus
26. The part of the oviduct that joins the uterus is [Pg-46,E]
(A) ampulla (B) isthmus (C) fimbriae (D) infundibulum
27. The uterus is also called [Pg-46,E]
(A) womb (B) cervix (C) cervical canal (D) none of these
28. The inner glandular layer that lines the uterine cavity is [Pg-46,E]
(A) perimetrium (B) myometrium (C) endometrium (D) ectometrium
29. The uterine layer that undergoes cyclical changes during menstrual cycle is [Pg-46,E]
(A) myometrium (B) endometrium (C) perimetrium (D) both (a) and (b)
30. Which uterine layer exhibits strong contractions during the delivery of the baby? [Pg-46,E]
(A) Endometrium (B) Perimetrium (C) Myometrium (D) Both (a) and (c)
31. The female external genitalia include [Pg-46,E]
(A) mons pubis (B) labia majora (C) clitoris (D) all of these
32. The opening of the vagina is often covered partially by a membrane called [Pg-46,E]
(A) hymen (B) clitoris (C) labia minora (D) none of these
33. A tiny finger-like structure which lies at the upper junction of the two labia minora is [Pg-46,E]
(A) hymen (B) mons pubis (C) clitoris (D) none of these
34. How many mammary lobes are found in each breast? [Pg-47,E]
(A) 20–25 (B) 15–20 (C) 10–15 (D) 25–30
35. The alveoli of mammary glands open into [Pg-47,E]
(A) mammary tubules (B) mammary duct
(C) lactiferous duct (D) mammary lobes
36. The milk is sucked out through [Pg-47,E]
(A) mammary duct (B) lactiferous duct (C) alveoli (D) none of these
37. Match the parts of female reproductive system given in Column-I with their
functions in Column-II and choose the correct option from the codes given below. [Pg-46,47,M]
Column I Column II
(a) Ovary (1) Delivery of baby
(b) Fimbriae (2) Steroid hormone
(c) Myometrium (3) Secretion of milk
(d) Cells of alveoli (4) Collection of ovum
a b c d
(A) 2 4 1 3
(B) 4 3 2 1
(C) 3 4 1 2
(D) 1 4 3 2
38. Match the layers of uterus given in Column-I with their characteristic features given in Column-II and choose the correct option from the codes given below. [Pg-46,M]
Column I Column II
(A) Perimetrium (1) Thick layer of smooth muscles
(B) Myometrium (2) Thick membranous layer
(C) Endometrium (3) Glandular layer
(4) Thin membranous layer
a b c
(A) 2 4 3
(B) 4 1 3
(C) 1 2 3
(D) 3 1 2
39. Match the parts of female external genitalia in Column-I with their characteristic features in Column-II. Choose the correct option from the codes given below. [Pg-46,M]
Column I Column II
(a) Mons pubis (1) Fleshy folds of tissue
(b) Labia majora (2) Cushion of fatty tissue
(c) Hymen (3) Tiny finger-like structure
(d) Clitoris (4) Covers opening of vagina
a b c d
(A) 2 1 4 3
(B) 4 3 2 1
(C) 1 4 3 2
(D) 2 1 3 4
40. The edges of the infundibulum possess finger like projections that -[Pg-45,M]
(A) are the sight of fertilisation.
(B) help in the collection of ovum after fertilisation.
(C) are responsible for the release of egg.
(D) none of these
41. Read the following statements about uterus and choose the correct option from the codes given below. [Pg-45,46,M]
(I) The shape of the uterus is like inverted pear.
(II) The uterus opens into vagina through a narrow cervix.
(III) The uterus along with cervix forms the birth canal.
(A) I and III (B) II and III (C) I and II (D) All of these
42. Read the following statements about mammary glands and choose the incorrect statement. [Pg-47,M]
(I) The mammary glands contain glandular tissue and fat.
(II) The mammary lobes of breasts contain alveoli which secrete milk.
(III) The milk secreted by alveoli is stored in lactiferous duct.
(A) Only II (B) Only III (C) Only I (D)I and III
43. Assertion: Ovaries are the primary sex organs.
Reason: Ovaries produce the female gamete. [Pg-44,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct, but reason is incorrect.
(D) Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
44. Assertion: Ovaries produce gamete as well as steroid hormones.
Reason: The oviducts, ovaries and cervix constitute the female accessory ducts. [Pg-44,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct, but reason is incorrect.
(D) Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
45. Assertion: The uterus opens into vagina through a narrow cervix.
Reason: The cavity of cervix is called cervical canal. [Pg-46,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct, but reason is incorrect.
(D) Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
46. Assertion: Mons pubis is a cushion of fatty tissue covered by skin and pubic hair.
Reason: The labia majora are paired folds of tissue under the labia minora. [Pg-46,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct, but reason is incorrect.
(D) Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
47. Assertion: The alveoli of mammary lobes open into their lumen.
Reason: Several lactiferous ducts join to form a mammary duct through which milk is sucked out.
[Pg-47,H](A) Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct, but reason is incorrect.
(D) Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Para-3.3
Gametogenesis
48. The process of producing gametes by primary sex organs is known as- [Pg-47,E]
(A) gametogenesis (B) spermatogenesis (C) oogenesis (D) none of these
49. The immature, diploid male germ cells that produce sperms are [Pg-47,E]
(A) spermatogonia (B) secondary spermatocytes
(C) spermatids (D) spermatozoa
50. Which of the following cells during gametogenesis is normally diploid? [AIPMT-2015] [Pg-47,M]
(A) Spermatid (B) Spermatogonia (C) Secondary polar body (D) Primary polar body
51. Among the following, identify the cell(s) which undergo mitotic division during spermatogenesis?
[Pg-47,E]
(A) Primary spermatocytes (B) Secondary spermatocytes
(C) Spermatids (D) Spermatogonia
52. Spermatogenesis is the process in which immature male germ cells undergo division to produce sperms. Choose the correct one with reference to above. [NCERT Exemplar] [Pg-47,H]
(A) Spermatogonia have 46 chromosomes and always undergo meiotic cell division.
(B) Primary spermatocytes divide by mitotic cell division.
(C) Secondary spermatocytes have 23 chromosomes and undergo second meiotic division.
(D) Spermatozoa are transformed into spermatids.
53. After spermiogenesis, sperm heads become embedded in [Pg-47,E]
(A) Leydig cells (B) antrum (C) Sertoli cells (D) interstitial cells
54. During spermiation the sperms are released from [NEET Exemplar] [Pg-47,E]
(A) seminiferous tubules (B) vas deferens
(C) epididymis (D) prostate gland
55. The difference between spermiogenesis and spermiation is [NEET-2018] [Pg-47,H]
(A) in spermiogenesis spermatids are formed, while in spermiation spermatozoa are formed.
(B) in spermiogenesis spermatozoa are formed, while in spermiation spermatids are formed.
(C) in spermiogenesis spermatozoa from Sertoli cells are released into the cavity of seminiferous tubules, while in spermiation spermatozoa are formed.
(D) in spermiogenesis spermatozoa are formed, while in spermiation spermatozoa are released from Sertoli cells into the cavity of seminiferous tubules.
56. Spermatogenesis starts due to significant increase in the secretion of [Pg-47,E]
(A) FSH (B) GnRH (C) LH (D) oxytocin
57. Refer to the given figure showing diagrammatic sectional view of a seminiferous tubule. In the figure, some parts are labeled as A, B, C and D. Identify the part which gets activated by FSH. [Pg-47,M]
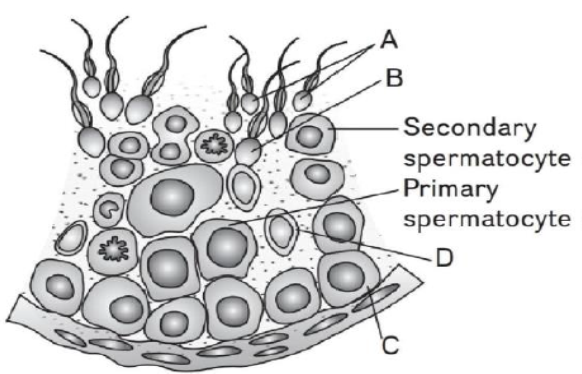
(A) A (B) B (C) D (D) C
58. Refer to the given flowchart. In it, some spaces are mentioned as A, B, C and D. Identify the correct option for them from the codes given below. [Pg-47,M]
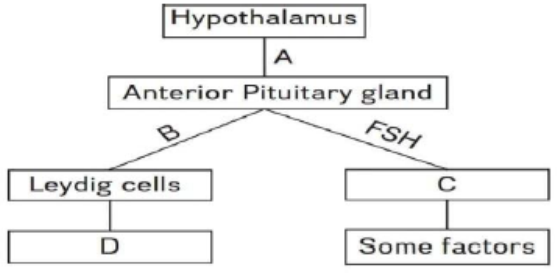
| A | GnRH | LH | Sertoli cells | Androgens |
| B | LH | GnRH | Androgens | Sertoli cells |
| C | Androgens | LH | Interstitial cells | FSH |
| D | FSH | Sertoli cells | GnRH | LH |
The anterior portion of the sperm head is covered by a cap-like structure called [Pg-48,E]
(A) middle piece (B) antrum (C) acrosome (D) none of these
60. Match the Column-I representing parts of the sperm to Column-II showing their functions and choose the correct option. [NCERT Exemplar] [Pg-48,M]
Column I Column II
(a) Head (1) Enzymes
(b) Middle piece (2) Sperm motility
(c) Acrosome (3) Energy
(d) Tail (4) Genetic material
A B C D
(A) 2 4 1 3
(B) 4 3 1 2
(C) 4 1 2 3
(D) 2 1 3 4
61. The semen of human male contains [Pg-49,E]
(A) seminal plasma (B) sperms (C) enzymes (D) both (a) and (b)
62. Refer to the given figure showing structure of a sperm. The figure is followed by four (I–IV) statements.
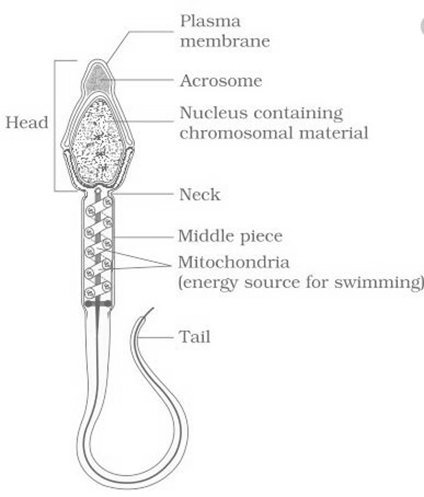
Choose the incorrect statement(s) about it. [Pg-48,M]
(I) The acrosome is filled with enzymes that help in fertilizing the ovum.
(II) The neck possesses numerous mitochondria.
(III) Tail is responsible for sperm motility.
(IV) The human male ejaculates 50–100 million sperms during a coitus.
(A) II and IV (B) I and III (C) I and II (D) III and IV
63. Which among the following has 23 chromosomes? [Pg-48,E]
(A) Spermatogonia (B) Zygote (C) Secondary oocyte (D) Oogonia
64. The oogenesis is markedly different from spermatogenesis because [Pg-48,E]
(A) it is initiated during embryonic development stage.
(B) it produces diploid gametes.
(C) it produces sperms also in special conditions.
(D) none of these
65. The tertiary follicle is characterized by a fluid filled cavity called [Pg-48,E]
(A) antrum (B) corpus luteum (C) matrix (D) none of these
66. In which stage primary oocyte completes its first meiotic division?
(A) Primary follicle (B) Secondary follicle (C) Tertiary follicle
67. Match Column-I with Column-II and choose the correct option from the codes given below.
[Pg-48,49,M]
Column I Column II
(a) Oogonia (1) Antrum
(b) Tertiary follicle (2) Gamete mother cells
(c) Secondary follicle (3) Haploid
(d) Secondary oocyte (4) More layers of granulosa
a b c d
(A) 4 3 2 1
(B) 1 2 3 4
(C) 2 1 4 3
(D) 3 4 2 1
68. Extrusion of second polar body from egg nucleus occurs [NEET 2019] [Pg-49,M]
(A) after entry of sperm, but before fertilisation (B) after fertilisation
(C) before entry of sperm into ovum (D) simultaneously with first cleavage
69. Refer to the given figure showing diagrammatic section view of ovary. The encircled part of figure is showing a process of oogenesis. Identify it as well as the follicle which is involved in this process.
[Pg-49,E]
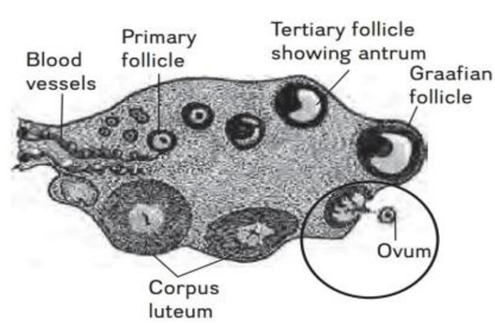
(A) Spermiation, Secondary follicle (B) Menstruation, Primary follicle
(C) Ovulation, Graafian follicle (D) Ovulation, Tertiary follicle
70. Assertion: Spermatogenesis starts at the age of puberty.
Reason: There is a significant increase in the secretion of gonadotropin releasing hormone at puberty.
[Pg-47,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation
(B) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false.
71. Assertion: Oogenesis is initiated at puberty.
Reason: Millions of oogonia are formed within each ovary every month. [Pg-48,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false.
72. Assertion: A large haploid secondary oocyte is formed due to unequal division.
Reason: A tiny second polar body is formed during this division. [Pg-48,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false.
Para-3.4
Menstrual Cycle
73. The reproductive cycle in the female primates is called [Pg-49,E]
(A) menstrual cycle (B) oestrous cycle (C) reproduction cycle (D) none of these
74 . Menarche that begins at puberty is [Pg-49,E]
(A) cessation of menstrual cycle (B) first menstruation
(C) period of pregnancy in which menstruation ceases (D) none of these
75. The cycle of events starting from one menstruation till the next one is called [Pg-49,E]
(A) menopause (B) menarche (C) menstrual cycle (D) oestrous cycle
76. The menstrual phase of menstrual cycle lasts for: [Pg-50,E]
(A) 8–15 days (B) 1–2 days (C) 1 day (D) 3–5 days
77. Menstrual flow results due to breakdown of [Pg-50,E]
(A) endometrial lining (B) blood vessels (C) myometrial lining (D) both (a) and (b)
78. Menstruation only occurs if [Pg-50,E]
(A) implantation has occurred (B) the released ovum is fertilized
(C) the released ovum is not fertilized (D) both (A) and (D)
79. The lack of menstruation may be due to [Pg-50,E]
(A) pregnancy (B) stress (C) poor health (D) all of these
80. The menstrual phase is followed by [Pg-50,E]
(A) follicular phase (B) luteal phase (C) secretory phase (D) both (b) and (c)
81. What change(s) occur in ovary and/or uterus during follicular phase of menstrual cycle? [Pg-50,E]
(A) Formation of Graafian follicle (B) Formation of corpus luteum
(C) Regeneration of endometrium (D) Both (A) and (C)
82. The changes in the ovary and uterus during proliferative phase are induced by changes in the levels of
[Pg-50,E]
(A) pituitary hormone (B) ovarian hormone (C) pineal hormone (D) both (a) and (b)
83. In the ovary of a healthy human female mature Graafian follicle is generally present around [NCERT Exemplar] [Pg-51,M]
(A) 5–8 day of menstrual cycle (B) 11–17 day of menstrual cycle
(C) 18–23 day of menstrual cycle (D) 24–28 day of menstrual cycle
84. During proliferative phase, the growing follicles secrete [Pg-51,E]
(A) LH (B) FSH (C) gonadotropins (D) estrogens
85. Refer to the given flowchart, in which three parts are labeled as A, B and C.
Identify them and choose the correct option from the codes given below. [Pg-51,M]
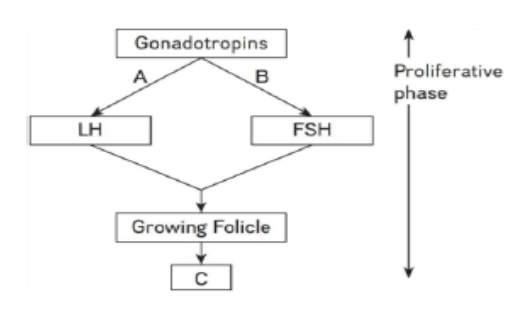
Codes-
A B C
(A) Increase Increase Estrogens
(B) Decrease Increase Estrogens
(C) Decrease Decrease Testosterone
(D) Increase Decrease TSH
86. Match the items given in Column-I with those in Column-II and select correct option from the codes given below. [NEET–2018] [Pg-51,M]
Column I Column II
(a) Proliferative phase (1) Breakdown of endometrial lining
(b) Secretary phase (2) Follicular phase
(c) Menstruation (3) Luteal phase
A b c
(A) 3 2 1
(B) 1 3 2
(C) 2 3 1
(D) 3 1 2
87. Both LH and FSH attain a peak level on about ‘A’ day of cycle. Choose the correct option for ‘A’.
[Pg-51,E]
(A) 10th day (B) 14th day (C) 19th day (D) 5th day
88. Read the following statements about LH surge and choose the incorrect one. [Pg-51,M]
(A) LH surge is rapid secretion of luteal hormone.
(B) It occurs in the mid of the cycle.
(C) LH surge induces degeneration of corpus luteum.
(D) It causes ovulation.
89. The release of ovum occurs during which phase of menstrual cycle? [Pg-51,E]
(A) Follicular phase (B) Proliferative phase (C) Ovulatory phase (D) Secretory phase
90. The ovulatory phase of menstrual cycle is followed by [Pg-51,E]
(A) luteal phase (B) follicular phase (C) proliferative phase (D) menstrual phase
91. No new follicles develop in the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle because [NEET Odisha-2019]
[Pg-51,M]
(A) Both FSH and LH levels are low in the luteal phase
(B) follicles do not remain in the ovary after ovulation
(C) FSH levels are high in the luteal phase.
(D) LH levels are high in the luteal phase.
92. Match the phases of menstrual cycle given in Column-I with the hormones secreted during that phase in Column-II. Choose the correct option from the codes given below. [Pg-50,51,M]
Column I Column II
(a) Follicular phase (1) Progesterone
(b) Ovulatory phase (2) Gonadotropins
(c) Luteal Phase (3) LH surge
(4) Estrogens
Codes
a b c
(A) 4 3,1 2
(B) 2,4 3 1
(C) 2 4,1 3
(D) 2 1 4,3
93. Among the following which change occurs during luteal phase? [Pg-51,E]
(A) Corpus luteum → Graafian follicle (B) Graafian follicle → Corpus luteum
(C) Primary follicle → Secondary follicle (D) Secondary follicle → Graafian follicle
94. Read the following statements about corpus luteum and choose the correct ones from the following options. [Pg-50,51,H]
(I) It is formed during ovulatory phase of menstrual cycle.
(II) It secretes large amounts of progesterone.
(III) In the absence of ovulation, the corpus luteum degenerates.
(IV) The degeneration of corpus luteum causes disintegration of endometrium.
(A) I and III (B) II and III (C) II and IV (D) I and IV
95. In human beings, permanent cessation of menstrual cycle is called: [Pg-51,E]
(A) Menopause (B) Menarche (C) Ovulation (D) None of these
96-97. Refer to the given figure to answer the question no 96–97. The figure is showing diagrammatic presentation of various events during a menstrual cycle. In the figure, A, B and C, D show the
levels of pituitary and ovarian hormones respectively.
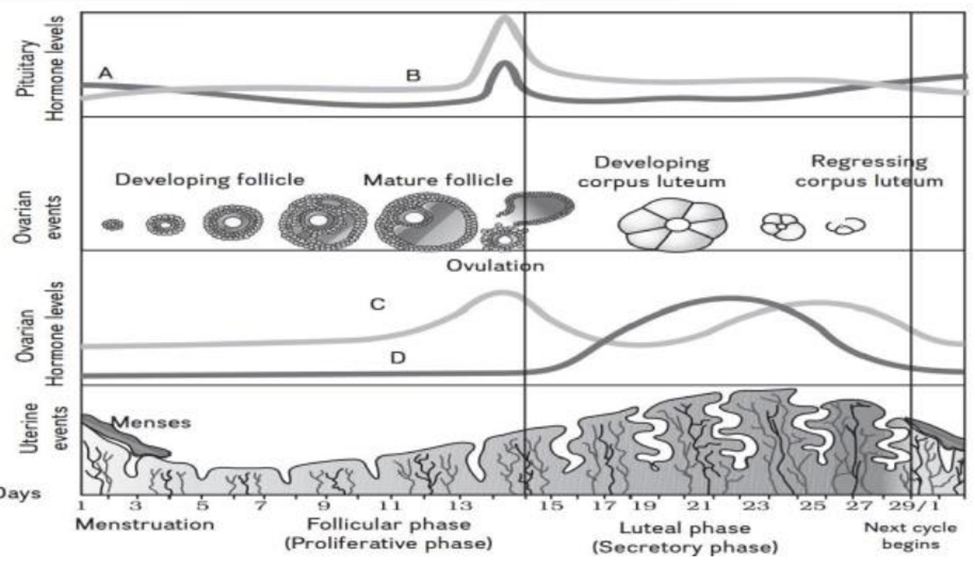
The gradual increase of which hormone stimulates the secretion of hormone C [Pg-50,E]
(A) A (B) B (C) D (D) Both (a) and (b)
97. The rapid increase of which hormone will induce rupture of Graafian follicle and thereby the release of ovum? [Pg-50,E]
(A) A (B) C (C) B (D) D
98. Choose the incorrect statement from the following. [NCERT Exemplar] [Pg-51,M]
(I) High levels of estrogen triggers the ovulatory surge.
(II) Oogonial cells start to proliferate and give rise to functional ova in regular cycles from puberty onwards.
(III) Sperms released from seminiferous tubules are poorly motile/non-motile.
(IV) Progesterone level is high during the post ovulatory phase of menstrual cycle.
(A) I and III (B) II and IV (C) I and IV (D) I and II
99. Consider the following features. [Pg-51,M]
(i) Transformation of Graafian follicle into corpus luteum.
(ii) Secretion of large amount of progesterone from corpus luteum.
(iii) Maintenance of endometrial lining of the uterus.
Select the correct phase of menstrual cycle that possesses all the above
characteristics.
(A) Follicular phase (B) Secretory phase (C) Proliferative phase (D) Ovulatory phase
100. Assertion: The lack of mensuration may be indicative of pregnancy.
Reason: Mensuration only occurs if the released ovum is not fertilised. [Pg-50,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false.
101. Assertion: During secretory phase the levels of LH and FSH gradually increase.
Reason: The increased levels of FSH and LH induce Graafian follicles to secrete progesterone.
[Pg-51,H]
- Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
( B) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false.
102. Assertion: During pregnancy, all events of the menstrual cycle stop.
Reason: In the absence of fertilisation, the corpus luteum degenerates. [Pg-51,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false.
Para-3.5
Fertilization and Implantation
103. The sperms released during copulation, finally reach to which part of the Fallopian tube? [Pg-51,E]
(A) Infundibulum (B) Isthmus (C) Ampulla (D) Ampullary-isthmic
104. All copulations not lead to the fertilisation and pregnancy. Choose the correct reason for the same from the following options. [Pg-51,M]
(A) Fertilisation can only occur if sperms are transported to the ampullaryisthmic junction before the ovum.
(B) Fertilisation can only occur if the ovum and sperms are transported simultaneously to the ampullaryisthmic junction.
(C) Fertilisation can only occur if ovum is transported to the ampullary–isthmic junction before the sperms.
(D) None of these
105. Capacitation occurs in [NEET–2017] [Pg-51,M]
(A) epididymis (B) vas deferens (C) female reproductive tract (D) rete testis
106. Capacitation refers to changes in the [AIPMT-2015] [Pg-51,M]
(A) ovum before fertilisation (B) ovum after fertilisation
(C) sperm after fertilisation (D) sperm before fertilisation
107. Refer to the given figure showing an ovum surrounded by few sperms. Sperm ‘A’ in the figure is trying to fertilise the ovum. How will this sperm ‘A’ ensure that no other sperm can fertilise the ovum?
[Pg-51,M]
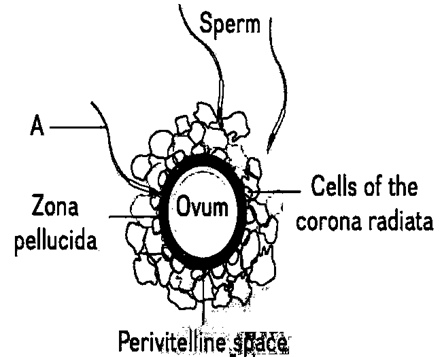
(A) By inducing changes in the cells of corona radiata.
(B) By inducing changes in the zona pellucida layer of the ovum.
(C) By inducing changes in the perivitelline space of the ovum.
(D) By releasing some chemicals to kill other sperms.
108. The membranous cover of the ovum that is found at the time of ovulation is [NCERT Exemplar]
[Pg-51,E]
(A) corona radiate (B) zona radiate (C) zona pellucida (D) chorion
109. During acrosomal reaction the sperm [NCERT Exemplar] [Pg-51,E]
(A) comes in contact with zona pellucida of the ova.
(B) undergoes reactions within the uterine environment of female.
(C) undergoes reactions within the epididymal environment of the male.
(D) produces androgens in the uterus.
110. The secretions of the acrosome help the sperm to enter into the cytoplasm of ovum through [Pg-51,E]
(A) corona radiata (B) zona pellucida (C) chorion (D) amnion
111. Match the events given in Column-I with their characteristic features in Column-II and choose the correct option from the codes given below. [Pg-52,M]
Column I Column II
(a) Fertilisation (1) Female reproductive tract
(b) Capacitation (2) Contact of sperm with zona pellucida
(c) Acrosomal reaction (3) Before fertilisation and after ovulation
(d) Second polar body (4) Ampullary – isthmic junction
Codes
a b c d
(A) 1 4 2 3
(B) 4 1 2 3
(C) 3 2 4 1
(D) 4 1 3 2
112. The embryo having 8–16 blastomeres is called [Pg-52,E]
(A) blastula (B) gastrula (C) morula (D) trophoblast
113. Morula is known as a developmental stage [NCERT Exemplar] [Pg-52,E]
(A) between the zygote and blastocyst (B) between the blastocyst and gastrula
(C) after the implantation (D) between implantation and parturition
114. Refer to the given flowchart. It has some blank spaces mentioned as A, B, C and D. Choose the correct option for these A, B, C and D. [Pg-51,52,H]
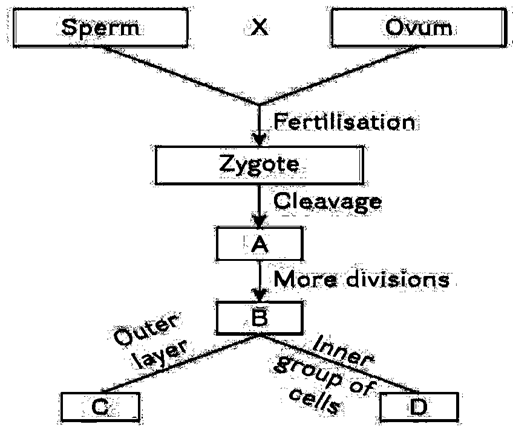
(A) Morula Blastocyst Trophoblast Inner cell mass (B) Blastocyst Morula Trophoblast Inner cell mass
(C) Morula Blastocyst Inner cell mass Trophoblast (D) Blastocyst Morula Inner cell mass Trophoblast
115. The blastomeres in the blastocyst are arranged into [Pg-52,E]
(A) an outer trophoblast and inner cell mass (B) an outer cell mass and inner trophoblast
(C) an outer cell mass and inner cell mass (D) none of these
116. During embryogenesis which part of blastocyst gets differentiated into embryo? [Pg-53,E]
(A) Trophoblast (B) Inner cell mass (C) Morula (D) Both (a) and (b)
117. The embedding of blastocyst in the endometrium of uterus is called [Pg-53,E]
(A) pregnancy (B) lactation (C) embryogenesis (D) implantation
118. Extrusion of second polar body from egg nucleus occurs [NEET–2015] [Pg-52,M]
(A) after entry of sperm but before fertilisation (B) after fertilisation
(C) before entry of sperm into ovum (D) simultaneously with first cleavage
119. All the haploid gametes produced by the female have [Pg-53,M]
(A) X-chromosomes
(B) Y-chromosomes
(C) 50% gametes have X and 50% have Ychromosomes
(D) 25% gametes have X and 75% have Ychromosomes
120. Cleavage that occurs in the zygote as it moves through the isthmus of oviduct towards the uterus is
[Pg-52,E]
(A) meiotic division v (B) mitotic division (C) reductional division (D) none of these
121. Match the following and choose the correct option from the codes given below. [Pg-52,533,M]
Column I Column II
(a) Trophoblast (1) Embedding of Blastocyst in the endometrium
(b) Cleavage (2) Group of cells hat would differentiate as embryo
(c) Inner cell mass (3) Outer layer of blastocyst attached to the endometrium
(d) Implantation (4) Mitotic division of zygote
Codes
a b c d
(A) 2 1 3 4
(B) 3 4 2 1
(C) 3 1 2 4
(D) 2 4 3 1
122. Refer to the given figure showing transport of ovum, fertilisation and passage of growing embryo through Fallopian tube. The figure is followed by four statements. Choose the incorrect statement about it. [Pg-52,M]
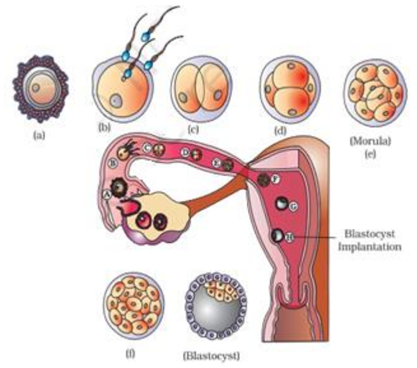
(A) The second meiotic division of secondary oocyte occurs after fertilisation.
(B) The embryo with 8–16 blastomeres is called morula.
(C) The trophoblast layer of blastocyst gets embedded in the endometrium.
(D) The cells of inner cell mass differentiate to form embryo.
123. Assertion: All copulations do not lead to fertilisation and pregnancy.
Reason: Fertilisation can only occur if the ovum and sperms are transported simultaneously to the ampullary– isthmic junction. [Pg-51,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false.
124. Assertion: The secretions of the acrosome help the sperm enter into the cytoplasm of the ovum.
Reason: The entry of sperm into the cytoplasm of the ovum is responsible for the capacitation of sperms. [Pg-51,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false.
125. Assertion: The blastomeres in the blastocyst are arranged into trophoblast and inner cell mass.
Reason: The trophoblast layer gets attached to the endometrium. [Pg-52,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false.
Para-3.6
Pregnancy and Embryonic Development
126. The finger-like projections that appear on called [Pg-53,E]
(A) trophoectoderm (B) chorionic villi (C) placenta (D) none of these
127. The structural and functional unit formed between the developing embryo (foetus) and maternal body is called [Pg-53,E]
(A) placenta (B) trophoblast (C) chorionic villi (D) trophoectoderm
128. The embryo remains connected to the placenta through [Pg-53,E]
(A) chorionic villi (B) trophoblast (C) umbilical cord (D) none of these
129. Choose the incorrect statement about placenta. [Pg-53,H]
(A) The placenta facilitates the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the embryo.
(B) It helps in the removal of CO2 and excretory/ waste materials produced by the embryo.
(C) The placenta is connected to the embryo through umbilical cord.
(D) Placenta acts like an endocrine tissue and produces several enzymes also.
130. Which of the following hormones is not secreted by human placenta? [NCERT Exemplar] [Pg-53,E]
(A) hCG (B) Estrogen (C) Progesterone (D) LH
131. Several hormones like hCG, hPL, estrogen, progesterone are produced by [NEET–2016] [Pg-53,E]
(A) Fallopian tube (B) pituitary (C) ovary (D) placenta
132. A hormone that is secreted by ovary in the later phase of pregnancy is [Pg-53,E]
(A) estrogen (B) FSH (C) relaxin (D) hCG
133. The hormone(s) that is/are produced during pregnancy only [Pg-53,E]
(A) hCG (B) hPL (C) relaxin (D) all of these
134. The levels of estrogens, progestogens, cortisol, prolactin, etc., increase many fold in blood during pregnancy. It is necessary for [Pg-53,M]
(A) supporting the fetal growth (B) metabolic changes in the mother
(C) the maintenance of pregnancy (D) all of these
135. Match Column-I with Column-II and choose the correct option from the codes given below. [Pg-53,M]
Column I Column II
(a) Chorionic villi (1) Secretes relaxin hormone
(b) Placenta (2) Finger-like projections on the trophoblast
(c) Umbilical cord (3) Structural and functional unit between foetus and mother
(d) Ovary (4) Connects embryo to placenta
Codes
a b c d
(A) 2 3 4 1
(B) 3 2 4 1
(C) 2 3 1 4
(D) 4 1 3 2
136. Immediately after implantation, which part of blastocyst differentiates into ectoderm and endoderm? [Pg-53,E]
(A) Trophoblast (B) Chorionic villi (C) Inner cell mass (D) None of these
137. Refer to the given figure showing human foetus within the uterus. How will the removal of ‘A’ in the figure affect the growth of foetus? [Pg-53,M]
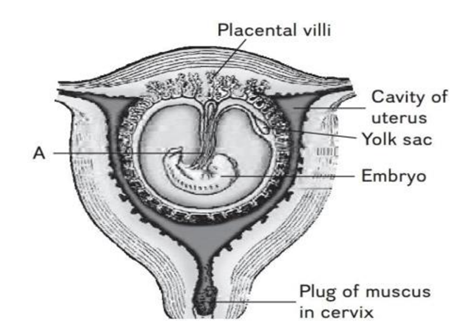
(A) Secretion of hCG hormone will stop
(B) Secretion of relaxin hormone will stop
(C) Transportation of substances to and from the embryo will stop
(D) All of these
138. The inner cell mass contains certain cells called stem cells which have the potency to give rise to
[Pg-54,E]
(A) specific tissues and organs (B) all tissues and organs
(C) only cardiac cells and heart (D) none of these
139. Match Column-I with Column-II and select the correct option using the codes given below.
[NEET–2016] [Pg-54,M]Column I Column II
(a) Mons pubis (1) Embryo formation
(b) Antrum (2) Sperm
(c) Trophectoderm (3) Female external genitalia
(d) Nebenkern (4) Graafian Follicle
Codes
a b c d
(A) 3 1 4 2
(B) 1 4 3 2
(C) 3 4 2 1
(D) 3 4 1 2
140. The foetus develops limbs and digits by the end of [Pg-54,E]
(A) 1st month of pregnancy (B) 2nd month of pregnancy
(C) 3rd month of pregnancy (D) 5th month of pregnancy
141. Match Column-I with Column-II and choose the correct option from the codes given below. [Pg-54,E]
Column I Column II
(Organ) (Month of development during pregnancy)
(a) Heart (1) Second month
(b) Limbs and digits (2) First month
(c) External genitalia (3) Fifth month
(d) Appearance of hair on head (4) Third month
Codes
a b c d
(A) 1 2 4 3
(B) 2 1 3 4
(C) 2 1 4 3
(D) 3 2 4 1
142. Read the following statements about major features of embryonic development at various months of pregnancy. Choose the incorrect statement(s) about it. [Pg-54,M]
(I) The embryo’s heart is the first formed organ.
(II) Most of the major organ systems are formed by the end of 2nd month of pregnancy.
(III) The first movement of foetus is observed during 7th month of pregnancy.
(IV) The eyelashes are formed by the end of second trimester.
(A) II and III (B) I and II (C) III and IV (D) Only IV
143. Select the correct sequences of events. [Odisha, NEET-2019] [Pg-54,M]
(A) Gametogenesis → Gamete transfer → Syngamy → Zygote cell differentiation → cell division (cleavage) → Organogenesis
(B) Gametogenesis → Gamete transfer → Syngamy → Zygote cell division (cleavage) → cell differentiation →organogenesis
(C) Gametogenesis → Gamete transfer → Syngamy → Zygote cell division (cleavage) → organogenesis → cell differentiation
(D) Gametogenesis → Syngamy → Gamete transfer → Zygote cell division (cleavage) → cell differentiation → organogenesis
144. Assertion: The placenta is connected to the embryo through an umbilical cord.
Reason: The umbilical cord helps in the transport of substances to and from the embryo. [Pg-53,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false.
145. Assertion: Placenta also acts as an endocrine gland.
Reason: In the later phase of pregnancy, relaxin is secreted by placenta. [Pg-53,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false.
146. Assertion: The first movements of foetus are observed during the third month of pregnancy.
Reason: By the end of first trimester, eyelids separate and eye-lashes are formed. [Pg-54,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false.
Para-3.7
Parturition and Lactation
147. The duration of pregnancy is called [Pg-54,E]
(A) parturition (B) lactation (C) gestation period (D) none of these
148. The process of delivery of the foetus is called [Pg-54,E]
(A) lactation (B) parturition (C) foetal ejection reflex (D) none of these
149. The signals for parturition originate from the [Pg-54,E]
(A) fully developed foetus (B) placenta (C) umbilical cord (D) both (A) and (B)
150. Match Column-I with Column-II and choose the correct option from the codes given below. [Pg-54,M]
Column I Column II
(a) Gestation period (1) Mild uterine contractions
(b) Parturition (2) Duration of pregnancy
(c) Foetal ejection reflex (3) Process of delivery of the foetus
(d) After birth (4) Placental expulsion
Codes
A b C d
(A) 2 3 1 4
(B) 2 4 1 3
(C) 4 3 2 1
(D) 1 2 3 4
151. The process of milk production is called [Pg-54,E]
(A) lactation (B) parturition (C) after birth (D) colostrum
152. Choose the incorrect statement from the following: [Pg-54,M]
(A) Parturition is induced by a complex neuroendocrine mechanism.
(B) The foetal ejection reflex triggers release of oxytocin from the hypothalamus.
(C) Oxytocin acts on the uterine muscles.
(D) The placenta is also expelled out of
153. Which of the following hormones is responsible for both the milk ejection reflex and the foetal ejection reflex? [Odisha, NEET-2019] [Pg-54,M]
(A) Relaxin (B) Estrogen (C) Prolactin (D) Oxytocin
154. The milk produced during the initial few days of lactation is called [Pg-54,E]
(A) colostrum (B) first milk (C) milky water (D) none of these
155. Choose the incorrect statement from the following. [NCERT Exemplar] [Pg-54,M]
(A) Internal fertilisation takes place, in birds and mammals.
(B) Colostrum contains antibodies and nutrients.
(C) Polyspermy is prevented by chemical changes on the egg surface.
(D) In the human female implantation occurs almost seven days after fertilisation.
156. Colostrum contains [Pg-54,E]
(A) antibodies (B) nutrients (C) enzymes (D) both (A) and (B)
157. Assertion: Parturition is a complex neuroendocrine mechanism.
Reason: The signals of parturition originate from the fully developed fetus and placenta. [Pg-54,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false.
158. Assertion: The mammary glands of the female undergo differentiation after parturition.
Reason: Lactation always starts after childbirth. [Pg-54,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false.
159. Assertion: Breast-feeding during the initial period of infant growth is recommended.
Reason: During initial few days after delivery, colostrum is produced. [Pg-54,H]
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true, but reason is false.
(D) Both assertion and reason are false
ANSWER KEY