NCERT LINE BY LINE QUESTIONS
2. Biological Classification
1. Choose the correct with respect to earliest for scientific basis of classification (Pg. 16, E)
A) It was proposed by Aristotle
B) Plants were divided as trees, shrubs & herbs on the basis of their morphological characters
C) Animals were classified into two groups that are those which have red blood and those that did not
D) All of these
2. Linnaeus system of classification did not deal with – (Pg. 16, E)
A) Eukaryotes and prokaryotes B) Unicellular & multicellular
C) Photosynthetic & non – photosynthetic D) All of these
3. How many kingdom according to five kingdom classification and Linnaeus system of classification is/are dedicated for prokaryotes exclusively (Pg. 16, E)
A) 1, 0 B) 1, 1 C) 2, 0 D) 3, 1
4. Moneran cell wall is composed by- (pg. 17, E)
A) Polysaccharide (Non cellulose) only B) Polysaccharide (cellulose)
C) Polysaccharide (chitin)
D) Amino acid and Non cellulosic polysaccharide
5. Chemosynthetic mode of nutrition is found is – (Pg. 17, E)
A) Monera B) Protist C) Plantae D) Fungi
6. R.H Whittaker classification is/are based upon – (Pg. 17, E)
A) Cell structure & body organization B) Mode of nutrition & reproduction
C) Phylogentic relationship D) All of these
7. Five kingdom classification was proposed in – (Pg. 17, E)
A) 1969 B) 1996 C) 1699 D) None of these
8. Choose the correct about 3 – domain system (Pg. 17, E)
A) Two domain are dedicated for prokaryotic while one domain is dedicated for eukaryotic
B) One domain is dedicated for prokaryotic while two domains are for eukaryotic
C) It has seven kingdom which are categorised in 3 – domain
D) It has six kingdom of which one kingdom is in first and third domain while 5 – kingdom is second domain.
9. Earlier classification system included bacteria, BGA (blue green algae) fungi, mosses, ferns under ‘Plants’ on basis of- (Pg. 17, E)
A) Mode of nutrition B) Body organisation & nuclear structure
C) Presence of cell wall D) Nature of cell wall.
10. How many of following are prokaryotes: (Pg. 17, E)
Bacteria, Mosses, ferns, fungi, pteridophyta, blue green algae, gymnosperms angiosperm
A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) More than 4
11. Fungi has cell wall composed of– (Pg. 17, E)
A) Cellulose B) Non – cellulosic + amino acid
C) Chitin D) Absence of cell wall
12. How many kingdom from R.H. Whittaker system does have exclusive autotrophic mode of nutrition
(Pg. 17, E)
A) Zero B) One C) Two D) Three
13. Unicellular eukaryotic are categorised in– (Pg. 17, E)
A) Monera B) Protista C) Plantae D) Animalia
14. How many of the following does belong to Protista (Pg. 18, E)
Amoeba, Spirogyra, Chlamydomonas, Chlorella, Paramecium
A) 5 B) 4 C) 3 D) 2
15. In five kingdom classification multicellularity began from – (Pg. 18, E)
A) Animalia B) Plantae C) Protista D) Fungi
Paragraph – 2.1
Kingdom Monera
16. Identify shape of bacteria (Pg. 18, E)
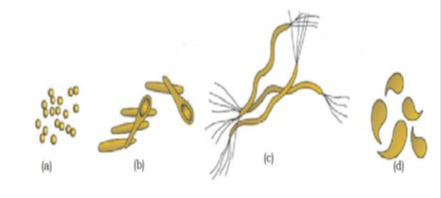
A) a = cocci, b = rod – shaped, c = bacilli, d = comma – shaped
B) a = spherical coccus, B = Bacilli, c = spirilla, d = vibrio
C) a = cocci, b = spirilla, c = vibrio, d = Bacilli
D) a = vibrio, b = spirilla, c = bacilli, d = coccus
17. choose the correct statement: (Pg. 18, E)
A) Bacteria are sole members of kingdom monera.
B) Bacteria are abundant macro – organism
C) Bacteria occurrence is limited to some area.
D) Bacteria can’t live in extreme habitat like desert
18. On the basis of shape; bacteria are grouped under_____ categories (Pg. 18, E)
A) Four B) Five C) Three D) None of these
19. Choose the correctly stated statement (Pg. 19, E)
A) Bacterial structure and behaviour are complex.
B) Bacterial structure and behaviour are simple
C) Bacterial structure is complex while behaviour is simple
D) Bacterial structure is simple while behaviour is complex
20. Synthesis of own food from inorganic substrate is occur in – (Pg. 19, E)
A) Autotrophic nutrition B) Chemosynthetic autotroph
C) Photosynthetic autotroph D) All of these
Paragraph – 2.1.1
Archaebacteria
21. Match the column – I & column – II (Pg. 19, M)
Column – I Column – II
(i) Halophiles (a) Marshy area
(ii) Thermoacidophiles (b) Salty area
iii) Methanogens (c) Hot springs
A) i) – c, ii) – b, iii – a B) i) – c, ii) – a, iii – b
C) i) – b, ii) – c, iii – a D) i) – b, ii) – a, iii – c
22. Archaebacteria differ from other bacteria in having – (Pg. 19, E)
A) Definite nuclear structure B) Cell wall structure
C) Adaptability cytoplasmic concentration D) Some membranous cell organelles
23. Survival of archaebacteria in extreme condition is achieved by – (Pg. 19, E)
A) Cell wall structure B) Some membranous cell organelles
C) Adaptability & cytoplasm D) All of these
24. Which of following statement is/are false (Pg. 19, M)
A) Methanogens are present in alimentary canal of several ruminant animals like cow & buffaloes
B) Methanogens are responsible for production of biogas from dung of ruminant animals
C) Methanogens are present in gut of several non – ruminant like cow & buffaloes
D) A & B
Paragraph – 2.1.2
Eubacteria
25. Label A , B and identify organism (c) (Pg. 19, E)
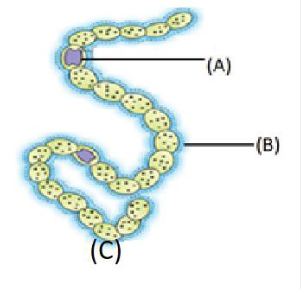
A) A = Heterocyst B = Mucilagenous sheath C = Nostoc, an archaebacteria
B) A = Heterocyst B = Mucilagenous sheath C = Nostoc
C) A = Mucilagenous, B = Heterocyst, C = Nostoc
D) A = heterocyst, B = Mucilagenous sheath, C = Nostoc, a filamentous algae
26. Choose the correct about blue green algae (Pg. 19, M)
i. Also known as cyanobacteria
ii. Presence of chlorophyll a, b similar to green plants
iii. Photosynthetic autotroph
iv) May be unicellular, colonial or filamentous
v. Occur in aquatic as well as terrestrial
A) i), iii), iv), v) B) i), ii), iii), iv), v) C) i), ii), iv), v) D) None of these
27. Nitrogen fixation is done by – (Pg. 19, E)
A) Specialised vegetative cell i.e. Heterocyst of Nostoc & Anabaena
B) Specialised reproductive cell i.e. Heterocyst of Nostac & Anabaena
C) Specialised vegetative as well as reproductive cell i.e. Heterocyst of Nostoc & Anabaena
D) None
28. Choose the wrong statement for chemosynthetic autotroph bacteria (Pg. 19, E)
A) They oxidise various inorganic substrate such as nitrates, nitrites & ammonia and use the released
Energy for their ATP production
B) They play great role in recycling nutrient like nitrogen phosphorous, iron & sulphur
C) For their energy production they utilize solar energy
D) They can prepare their food from inorganic substrate.
29. Citrus canker is – (Pg. 20, E)
A) Plant disease cause by bacteria B) Human disease cause by bacteria
C) Pet disease cause by bacteria D) None of these
30. Which of following is not economic importance of heterotrophic bacteria (Pg. 19, E)
A) Making curd from milk B) Antibiotic production
C) N2 fixing in legumes root D) N2 fixing in Anabaena
31. Choose the incorrect option about bacterial reproduction – (Pg. 19, E)
A) Bacteria reproduce mainly by fission
B) Under unfavourable condition they produce spores
C) They also reproduce by sexual reproduction
D) They show a sort of sexual reproduction
32. Here are few statement given below, Identify organism on basis of statement (Pg. 20, M)
i. Lack cell wall ii. Smallest living cell known
iii. Can survive without oxygen iv. Pathogenic in animal & plants.
A) Nostoc B) Anabaena C) Mycoplasma D) Chlorella
Paragraph – 2.2
Kingdom Protista-Introduction
33. Protista includes – (Pg. 20, E)
A) Unicellular prokaryotes B) Bacteriophages
C) Unicellular eukaryotes D) B.G.A
34. Which of the following kingdoms has no well defined boundaries? (Pg. 20, E)
A) Monera B) Protista C) Fungi D) Metaphyta and Metazoa
35. Members of Protista are primarily (Pg. 20, E)
A) Parasites B) Terrestrial C) Aquatic D) Photosynthetic
36. Nearly all protists are – (Pg. 20, E)
A) Aerobic B) Anaerobic
C) Aerobic or anaerobic D) Photosynthetic
37. Nutritionally, protists are- (Pg. 20, E)
A) Photoautotrophs B) Heterotrophs
C) Saprotrophs D) Photoautotrophs, heterotrophs or autotrophs
38. Based upon the modes of nutrition, protists are grouped into – (Pg. 20, E)
A) Plant-like protists (algae) and ingestive, animal-like protists (protozoa); and absorptive, fungus like protists
B) Chrysophytes, Dinoflagellates and Euglenoids only
C) Slime moulds and fungi only
D) Flagellated protozoans and sporozoans only
39. Which of the following are placed under Protista-? (Pg. 20, E)
A) Chryosophytes and Dinoflagellates B) Euglenoids
C) Slime moulds and protozoans D) All
40. Locomotory structures in protists are – (Pg. 20, E)
A) Flagella B) Cilia C) Pseudopodia D) All
41. Protista form a link with – (Pg. 20, E)
A) Plants only B) Animals only C) Fungi only D) Plants, animals and fungi
Paragraph – 2.2.1
Chrysophytes
42. Chrysophytes include – (Pg. 20, E)
A) Diatoms and desmids (golden algae) B) Euglenoids
C) Dinoflagellates D) Slime moulds
43. Which of the following modes of reproduction can be found in at least some protists? (Pg. 20, E)
A) Binary fission B) Sexual reproduction
C) Spore formation D) All
44. Select the following statement that does not apply to diatoms – (Pg. 20, E)
A) Diatom cell wall may be impregnated with silicon
B) Cell wall is made up of 2 half-shells fit tightly together
C) Diatom is a chrysophyte D) Diatom is multiflagellate
45. Silica gel (Keieselghur)/Diatomite/Diatomaceous earth is obtained by – (Pg. 20, E)
A) Diatoms B) Dinoflagellates C) Euglenoids D) Brown algae
46. The diatoms do not easily decay like most of the other algae because – (Pg. 20, E)
A) They have highly siliceous wall B) They have water proof cells
C) Their cell wall are mucilaginous D) Cell wall is virus-resistant
47. Diatomaceous earth is used for all except (Pg. 20, E)
A) Polishing B) Filtration of oils and syrups
C) Sound and fire proof room D) Biogas
48. Chrysophytes are – (Pg. 20, E)
A) Planktons B) Nektons C) Benthonic D) Active swimmers
49. Chief producers in ocean are – (Pg. 20, E)
A) Dinoflagellates B) Diatoms C) Euglenoids D) Green algae
50. Photosynthetic protists are – (Pg. 20, E)
A) Euglenoids, Diatoms and Dinoflagellates B) Euglenoids and slime moulds
C) Diatoms and Zooflagellates D) Desmids +Ciliates
Paragraph – 2.2.2
Dinoflagellates
51. Dinoflagellates are mostly- (Pg. 21, E)
A) Marine B) Fresh water C) terrestrial D) Saprophytes
52. Red tides in warm coastal water develop due to super abundance of- (Pg. 21, E)
A) Dinoflagellates B) Euglenoid forms
C) Diatoms and desmids D) Chlamydomonas nivalis
53. Red tide is caused by – (Pg. 21, E)
A) Ceretium B) Noctiluca C) Gonyaulax D) All of these
54. Dinoflagellates have – (Pg. 21, E)
A) A single flagellum in the transverse groove between the cell plates
B) A single flagellum in the longitudinal groove between the cell plates
C) Two flagella one lies longitudinally and the other transversely in a furrow between the wall plates
D) No flagella
55. In which of the following the cell wall has stiff cellulose plate on the outer surface – (Pg. 21, E)
A) Dinoflagellates B) Desmids C) Diatoms D) Euglenoids
56. Which of the following releases toxins that may even kill other marine animals like fishes –
(Pg. 21, E)
A) Gonyaulax B) Paramecium C) Euglenoids D) Sporozoans
Paragraph – 2.2.3
Euglena
57. Euglenoids e.g. Euglena are found – (Pg. 21, E)
A) In fresh running water B) In fresh stagnant water
C) In marine environment D) In both fresh and marine water
58. Which of the following statements about Euglena is true? (Pg. 21, E)
A) Euglenoids are flagellates
B) Euglena placed in continuous darkness loses their photosynthetic activity and die
C) The pigments of Euglena are quite different from those of green plants
D) Euglena is a marine protist
59. Which of the following statement is true about Euglena? (Pg. 21, E)
A) They show flagellar locomotion B) They have a rigid cell wall
C) They have no chloroplast D) They are obligate autotroph
60. (Pg. 21, E)
i. Instead of a cell wall they have a protein rich pellicle making their body flexible.
ii. They have 2 flagella, a short and a long one.
iii. They have mixotrophic nutrition
iv. In light they are photosynthetic, but act as heterotroph (predating other smaller organism) when they are in dark.
v. They are connecting link between plants and animals.
The above statements are assigned to –
A) Dinoflagellates B) Slime mould
C) Desmids and Diatoms D) Euglena
Paragraph – 2.2.4
Slime Moulds
61. Slime moulds – (Pg. 21, E)
A) Are parasite B) Do not produce fruiting bodies
C) Do not produce spores D) Saprophytic protists
62. The slimy mass of protoplasm with nuclei forms the body of slime moulds is called –
(Pg. 21, E)
A) Plasmodium B) Myxamoeba C) Sporocytes D) Periplasmodium
63. Which of the following is correct about the slime mould? (Pg. 21, E)
I. Its thalloid body, plasmodium, has pseudopodia for locomotion and engulfing organic matter
II. During unfavourable conditions plasmodium differentiates and produces fruiting bodies, sporangium
III. Spores possess no true cell wall.
IV. They are dispersed by air current.
V. Being extremely resistant, spores survive for many years
VI. Plasmodium can grow upto several feet.
A) I, II, IV, V, VI B) I, II , III C) I, II , III, VI D) II, III , VI
Paragraph – 2.2.5
Protozoans
64. Protozoans are not included in kingdom Animalia because – (Pg. 22, E)
A) Mostly asymmetrical B) Unicellular eukaryotes
C) Heterotrophic nature D) Multicellular prokaryotes
65. All protozoans are – (Pg. 22, E)
A) Saprophytes only B) Parasites only
C) Predators only D) Heterotrophs (parasites or predator) only
66. Which of the following is considered to be primitive relatives of animals -? (Pg. 22, E)
A) Dinoflagellates B) Slime moulds
C) Protozoa D) Protochordata
67. How many major groups protozoan have? (Pg. 22, E)
A) 3 B) 4 C) 2 D) 8
68. Which of the following are protozoans? (Pg. 22, E)
A) Diatoms, flagellates, ciliates B) Desmids, flagellates, ciliates
C) Amoeboid, flagellates, ciliates, sporozoans
D) Amoeba, ·Paramecium, dinoflagellates, Plasmodium
69. Which of the following statements is wrong about the amoeboid protozoans? (Pg. 22, M)
A) They live in freshwater, sea water or moist soil
B) Amoeba has pseudopodia for locomotion and capture prey
C) Entamoeba show holozoic nutrition
D) Marine forms are shelled with silica
70. Flagellated protozoans are – (Pg. 22, E)
A) Free living B) Parasites
C) Either free living or parasites D) Pseudopodia
71. Which one is correct about Trypanosoma?
A) They are flagellated protozoan B) They are parasite
C) They cause sleeping sickness D) All
72. Paramecium- (Pg. 22, E)
A) Is a ciliated protozoan
B) Shows water current movement by cilia which helps the food to be steered into gullet
C) Has a cavity (gullet) that opens to the outside of the cell surface
D) All
73. Plasmodium (malarial parasite) (Pg. 22, E)
A) Is a ciliated protozoan
B) Shows water current movement by cilia which helps the food to be steered into gullet
C) Causes malaria D) All
74. Which of the following always produce an infectious spore like stage in their life cycles?
A) Ciliated protozoans B) Flagellated protozoans (Pg. 22, E)
C) Sporozoans D) None
Paragraph – 2.3
Kingdom Fungi – Introduction
75. Mode of nutrition in fungi is not – (Pg. 22, E)
A) Parasitic B) Saprophytic C) Autotrophic D) Heterotrophic
76. All of the following are fungi except – (Pg. 22, E)
A) Yeast B) Penicillium C) Plasmodium D) Puccinia
77. Which of the following is odd? (Pg. 22, E)
A) Toad stool B) Puccinia C) Alternaria D) Mushroom
78. Cell walls of all fungi consist of the polysaccharide – (Pg. 22, E)
A) Chitin B) Cellulose C) Silica D) Pectin
79. The body of multicellular fungus is called a – (Pg. 22, E)
A) Monokaryon B) Hyphae C) Rhizoids D) Dikaryon
80. The cells of the body of a multicellular fungus are organised into rapidly growing individual filaments called – (Pg. 22, E)
A) Mycelium B) Rhizoids C) Hyphae D) Dikaryon
81. Which one is unicellular fungus? (Pg. 22, E)
A) Puccinia B) Toad stool C) Penicillium D) Yeast
82. Coenocytic hypha is – (Pg. 22, E)
A) Uninucleate hypha B) Multicellular hypha
C) Multinucleate hypha without septae D) Hypha in coelom
83. Many fungi are in ____ association with photosynthetic organisms to form mycorrhizae or lichens –
(Pg. 22, E)
A) Parasitic B) Symbiotic C) Photosynthetic D) Saprobic
84. Fungi can be parasites on – (Pg. 22, E)
A) Animals B) Human being C) Plants D) All
85. Fungi prefer to grow in – (Pg. 22, E)
A) Cold and dry places B) Hot and dry places
C) Sea water D) Warm and humid places
86. Fungi occur- (Pg. 22, E)
A) In air and soil B) In water
C) On plants and animals D) All
87. Fungi show a great diversity in – (Pg. 22, E)
A) Morphology B) Habitat
C) Both a and b D) Nutrition
88. Reproduction in fungi can take place by all of the following vegetative methods except-
(Pg. 22, E)
A) Gemmae B) Fragmentation C) Fission D) Budding
89. Fungi show asexual reproduction by all of the following spores except- (Pg. 23, E)
A) Conidia B) Oospore C) Sporangiospore D) Zoospores
90. Sexual reproduction in fungi is by all of the following except- (Pg. 23, E)
A) Oospores B) Ascopores C) Zoospores D) Basidiospores
91. Select the correct statements below that correctly apply to the Kingdom Fungi- (Pg. 23, E)
A) Some fungi form beneficial interrelationships with plants
B) Certain fungi are natural sources of antibiotics
C) The fungal life cycle typically includes a spore stage
D) All
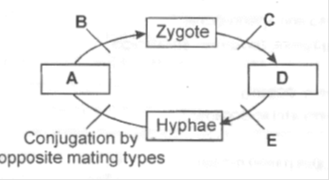
93. The above diagram shows a generalized life cycle of a fungus. The appropriate terms for A to E are-
(Pg. 23, H)
A) Spores are absent in air B) Spores are present in the bread
C) Spores are in the air D) The bread gets decomposed·
94. Which of the following is the correct sequence of 3 steps in the sexual cycle of fungi- (Pg. 23, E)
A) Mitosis —-. Meiosis —-. Fertilization
B) Plasmogamy—-. Karyogamy—-. Meiosis
C) Meiosis —-. Plasmogamy —-. Karyogamy
D) Karyogamy—-. Plasmogamy—-. Meiosis
95. Fungi are classified on the basis of – (Pg. 23, E)
A) Morphology of mycelium B) Development of fruiting bodies
C) Mode of spore formation D) All
96. Dikaryophase I Dikaryon formation is a specific characteristic of- (Pg. 23, E)
A) All fungi B) Phycomycetes and ascomycetes
C) Only basidiomycetes D) Ascomycetes and basidiomycetes
97. Coenocytic, multinucleate and branched mycelial habit is found in- (Pg. 23, E)
A) Basidiomycetes B) Phycomycetes
C) Ascomycetes D) Deuteromycetes
9 8. Column I Column II
A. Phycomycetes I. Sac fungi
B. Ascomycetes II. Algal fungi
C. Basidiomycetes III. Fungi imperfecti
D. Deuteromycetes IV. Club fungi
The correct matching is – (Pg. 23, H)
A) A-II, B-I, C- IV, D-III B) A- II, B – IV, C – I, D – III
C) A- IV, B – I, C – II, D – III D) A- IV, B – III, C – II, D – I
Paragraph – 2.3.1
Phycomycetes
99. Members of phycomycetes are found- (Pg. 23, E)
I. In aquatic habitat II. On decaying wood
III. On moist and damp places IV. As obligate parasite on plants
A) None of the above B) I and IV
C) II and III D) All of the above
100. In phycomycetes asexual reproduction occurs by- (Pg. 23, E)
A) Zoospores (motile) B) Aplanospores (non-motile)
C) Both D) Aplanogamete
101. Which of the following spores are produced endogenously? (Pg. 23, E)
A) Zoospores and Conidia B) Conidia and aplanospores
C) Aplanospores and zoospores D) Aplanospore, zoospores and conidia
102. In Phycomycetes sexual reproduction occurs by (Pg. 23, E)
A) Isogamy and anisogamy B) lsogamy, oogamy
C) Isogamy, anisogamy and oogamy D) Oogamy and anisogamy
103. All the following belong to phycomycetes except – (Pg. 23, E)
A) Penicillium B) Rhizopus (bread mould)
C) Mucor D) Albugo
104. Which of the following is parasite on mustard? (Pg. 23, E)
A) Albugo B) Puccinia C) Yeast D) Ustilago
Paragraph – 2.3.2
Ascomycetes
105. Which of the following is false about ascomycetes? (Pg. 23, E)
A) Mode of nutrition saprophytic, decomposer, coprophilous (growing on dung) and parasitic
B) Includes unicellular (e.g. yeast) and multicellular forms
C) Mycelium is coenocytic
D) Aspergillus, Claviceps, Neurospora are important members of Ascomycetes
106. I. It includes unicellular as well as multicellular fungi
II. In multicellular forms hyphae are branched and septate
III. Conidiophore produces conidia (spores) exogenously in chain
IV. Sexual spores are ascopores produced endogenously in Ascus
V. Fruiting body is called ascocarp
Which of the above characters are show by -? (Pg. 23, E)
A) Phycomycetes B) Sac fungi C) Club fungi D) Fungi imperfecti
107. Which of the following are edible ascomycete’s delicacies? (Pg. 24, E)
A) Morels+ Mushroom B) Truffles+ Toadstool
C) Morels+ Truffles D) Puffball+ Mushroom
108. Which of the following is used extensively in biochemical and genetical work? (Pg. 24, E)
A) Agaricus B) Alternaria C) Neurospora D) Mucor
109. Which of the following ascomycetes is the source of antibiotic? (Pg. 24, E)
A) Neurospora B) Penicillium C) Claviceps D) None
Paragraph – 2.3.3
Basidiomycetes
110. Basidiomycetes include – (Pg. 24, E)
A) Mushroom, Toadstool, Puffball and bracket fungi
B) Smut fungi and rust fungi
C) Both a and b
D) Bread mould, sac fungi and algal fungi
111. Which of the following are common parasite basidiomycetes (Pg. 24, E)
A) Puccinia (rust) and Ustilago (smut) B) Sac fungi
C) Puffballs D) Agaricus (mushroom)
112. Where does meiosis occur in mushroom?
A) Basidiospore B) Basidium C) Basidiocarp D) Ascus mother cell
113. I. Mycelium is branched and septate
II. No asexual spores are generally formed
III. Vegetative reproduction by fragmentation is common
IV. Sex organs are absent but sexual reproduction takes place by somatogamy
V. Karyogamy and meiosis occur in basidium to form haploid exogenous 4 basidiospores
VI. Basidia are arranged in basidiocarp.
The above characters are assigned to – (Pg. 24, E)
A) Sac fungi B) Club fungi C) Algal fungi D) Fungi imperfect
114. Plasmogamy in fungi is the fusion of- (Pg. 24, E)
A) Two haploid gamete cells and their nuclei at once
B) Two haploid nuclei
C) Two haploid gamete cells
D) Two diploid vegetative cells with nuclei
115. Karyogamy is – (Pg. 24, E)
A) Fusion of two protoplasts
B) Fusion of two nuclei
C) Fusion of two plasma membranes
D) All of these
Paragraph – 2.3.4
Deuteromycetes
116. Which of the following is false about deuteromycetes? (Pg. 24, E)
A) They reproduce only by asexual spores (conidia)
B) Mycelium is branched and septate
C) They have only parasitic forms
D) They have no sexual stage (perfect stage)
117. Which of the following is correct about class Deuteromycetes? (Pg. 24, E)
A) Some members are saprophytes or parasites
B) A large number of members are decomposers of litter and help in mineral cycling
C) Alternaria, Colletotrichum and Trichoderma are deuteromycetes
D) All
118. Sexual reproduction is found in all except (Pg. 24, E)
A) Deuteromycetes B) Ascomycetes
C) Phycomycetes D) Basidiomycetes
119. If sexual stage is discovered in a member of deuteromycetes, it is moved to- (Pg. 24, E)
A) Phycomycetes B) Basidiomycetes
C) Ascomycetes D) Both band c
Diagram Based Questions
120. Identify the diagram. (Pg. 23, E)
(A) (i) Mucor (ii) Aspergillus (iii) Agaricus
(B) (i) Aspergillus (ii) Mucor (iii) Agaricus
(C) (i) Agaricus (ii)Aspergillus (iii) Mucor
(D) (i) Agaricus (ii) Mucor (iii) Aspergillus
121. Identify the diagram. (Pg. 21, E)

A) (i) Dinoflagellates (ii) Euglena
B) (i) Dinoflagellates (ii) Paramoceium
C) (i) Euglena (ii) Dinoflagellates
D) (i) Slime mould (ii) Paramecium
122. Kingdom plantae includes- (Pg. 25, E)
i. All eukaryotic chlorophyllous organisms
ii. Some prokaryotic chlorophyllous organisms
iii. Few eukaryotic partial heterotrophic plant
iv. Few prokaryotic partial heterotrophic plant
A) i, iii B) ii, iv C) i, ii, iii D) i, iii, iv
123. Plantae does not includes how many of following- (Pg. 25, E)
Algae, Fungi, Bryophyte, Bladderwort, Pteridophyta, Gymnosperm, Angiosperm
A) Zero B) One C) Two D) Three
124. Life cycle of angiosperms plant have- (Pg. 25, E)
A) Diploid sporophyte & diploid gametophyte
B) Diploid gametophyte & haploid sporophyte
C) Diploid sporophyte & haploid gametophyte
D) Haploid sporophyte & haploid gametophyte
125. How many of following enlisted are correct about plantae- (Pg. 25, E)
I. Cells have eukaryotic structure
II. Prominent chloroplast
III. Cellulosic cell wall
IV. Life cycle has three distinct phase
V. Show alteration of generation
A) One B) Two C) Three D) Four
Paragraph – 2.5
Kingdom Animalia
126. Kingdom Animalia are characterized by (Pg. 25, E)
A) Heterotrophic eukaryotic unicellular & multicellular organism that lack cell wall
B) Holozoic ,digest food in an internal cavity and store food as complex carbohydrates or fat
C) Higher as well as lower forms show elaborate sensory mechanisms
D) All of the above
127. How many of following term is correct about Animalia- Heterotroph, eukaryotic, prokaryotic, unicellular, multicellular, store food as glycogen, presence of elaborated neuromotor mechanism
without any exception, embryological development (Pg. 25, E)
A) 6 B) More than 6 C) 5 D) Less than 3
Paragraph – 2.6
Viruses, viroids, prions, & lichens
128. In R.H Whittaker system, viroids, prions & lichens are grouped into- (Pg. 25, E)
A) Monera B) Protista
C) Protista and fungi D) None of these
129. Viruses did not place in classification due to- (Pg. 25, E)
A) Lack in study of viruses
B) They are not considered truly ‘living’
C) Lack of genetic material
D) All of these
130. Viruses are not- (Pg. 25, E)
A) Non-cellular organism
B) Inert crystalline structure outside the living cell
C) Active crystalline structure outside the living cell
D) Once they infect a cell they take over the machinery of host cell to replicate themselves, killing the host
131. The name viruses-
A) which means venom was given by Dmitri Ivanowsky
B) which means venom was given by M.W. Beijerinek
C) which means venom was given by Stanley
D) which means venom was given by Pasteur
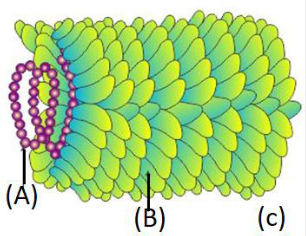
Identify a, b & organism(c)
A) a=DNA, b=capsid, c=TMV B) a=RNA, b=capsid, c=TMV
C) a=capsid, b=DNA, c=bacteriophage D) a=capsid, b=RNA, c=bacteriophage
133. choose the correct statement –
A) genetic material of mosaic disease of tobacco causing organism is DNA
B) Viruses were found to be smaller than bacteria but they can passed through bacteria proof filters
C) M.W Beijerinek (1898) demonstrated that the extract of infected plant of tobacco could cause infection in healthy plants
D) Viruses were found to be smaller than bacteria and they can passed through bacteria proof filters.
134. Contagium vivum fluidum was stated by – (Pg. 26, E)
A) Dmitri lavanowsky (1898) B) M.W. Beijerinek (1892)
C) W.M. Stanley (1935) D) None of these
135. Who showed that viruses could be crystallized & crystals outside host-
A) W.M. Stanley(1935) B) M.W.Beijerinek (1898)
C) Dmitri lvanowsky (1892) D) M.W. Stanley (1898)
136. Which of following is major constituent in crystallined virus structure – (Pg. 26, E)
A) Carbohydrate B) Protein C) Fat D) Nucleic acid
137. Viruses are (Pg. 26, E)
A) Autotroph B) Obligate parasite C) Saprotroph D) Holozoic
138. Genetic material of viruses are/is – (Pg. 26, E)
A) DNA B) RNA
C) DNA and RNA both in an individual virus
D) DNA or RNA in an individual virus
139. The infection material of viruses is/are (Pg. 26, E)
A) Protein coat B) Genetic material
C) Nucleoprotein D) All of these
140. In general viruses that infect plants have- (Pg. 26, E)
A) ds RNA B) ss RNA C) ds DNA D) ss DNA
141. Animal infection viruses are not generally (Pg. 26, E)
A) ss RNA B) ds RNA C) ds DNA D) ss DNA
142. genetic material of bacteriophage is – (Pg. 26, E)
A) ds DNA B) ss RNA C) ds RNA D) ss DNA
143. bacteriophage is – (Pg. 26, E)
A) bacteria that infect virus
B) virus that infect bacteria
C) bacteria that infect cellular organism
D) virus that infect other than bacteria
144. The protein coat called ___(A)___ made of small subunit called ____(B)____ that protect ____(C)____ of virus (Pg. 26, E)
A) A = capsomere, B = capsid, C= genetic material
B) A = capsid, B = capsomere, C = genetic material
C) A = capsid, B = capsomere, C = enzyme and mineral
D) A = capsomere, B = capsid, C = enzyme and mineral
145. Head of bacteriophage is – (Pg. 26, E)
A) Helical B) Polyhedral C) Icosahedral D) A & B
146.
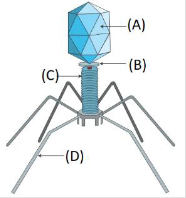
A) A = head B = sheath, C = tail fibers, D = Collar
B) A = head B = collar C = sheath, D = tail fibers
C) A = collar B = head C = tail fibers D = sheath
D) A = tail fibers B = sheath C = head D = collar
147. Viroid was discovered by –
A) T.O. Diener (1971) (Pg. 27, E)
B) W.M. Stanley (1935)
C) T.O diener (1935)
D) W.M. Stanley (1971)
148. Choose the correct on basis of size : (Pg. 27, E)
A) Bacteria<virus<viroid B) Viroid<virus<bacteria
C) Viroid>bacteria<virus D) Bacteria>viroid>virus
149. Given below are statement (i-vi) choose correct set (Pg. 27, E)
i. Viroid=virus-capsid ii. Potato spindle disease cause by prions
iii. Viroid have free DNA iv. Viroid have free RNA
v. DNA of viroid was of low molecular weight
iv. RNA of viroid was of light molecular weight
A) i,iv only B) i, vi, iii C) i, iv, vi D) i, iii, v
150. Prion cause- (Pg. 27, E)
A) BSE in cattle and CJD in human
B) BSE in human and CJD in cattle
C) BSE and CJD cause in cattle
D) BSE and CJD cause in human
151. Prions are- (Pg. 27, E)
A) Smaller than virus B) Larger than virus
C) Smaller than viroid D) Similar in size to viruses
152. Choose the incorrect about BSE (Pg. 27, E)
A) It expanded as Bovine spongiform encephalophathy
B) Caused by prion
C) Its analogous variant is CJD
D) Its homologous variant is CJD
153. Lichen are – (Pg. 27, E)
A) Saprotroph only B) Symbiotic
C) Parasitic only D) A & C
154. Lichen are mutual association of- (Pg. 27, E)
A) Mycobiont (fungal) and phycobiont (algae)
B) Gymnosperm root & fungi
C) Algae & gymnosperm root
D) All of these
155. Mycobiont and phycobiout are ___&___ respectively (Pg. 27, E)
A) Autotrophic & heterotrophic
B) Autotrophic & autotrophic
C) Heterotrophic & autotrophic
D) Heterotrophic & heterotrophic
156. The function of fungal part is lichen is/are (Pg. 27, E)
A) Water absorption B) Mineral absorption
C) Provide shelter D) All of these
157. Lichen cannot grow in – (Pg. 27, E)
A) Polluted area B) Area where there is no pollution
C) Association between fungi and algae is unpolluted region
D) All of these
NEET PREVIOUS YEARS QUESTIONS
1. Select the incorrect statement. [2018]
(a) Cell wall is present in members of fungi and plantae.
(b) Mushrooms belong to basidiomycetes.
(c) Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell in all kingdoms except monera.
(d) Pseudopodia are locomotory and feeding structures in sporozoans.
2. Which among the following is not a prokaryote? [2018]
(a) Saccharomyces (b) Mycobacterium (c) Oscillatoria (d) Nostoc
3. Ciliates differ from all other protozoans in [2018]
(a) using flagella for locomotion.
(b) having a contractile vacuole for removing excess water.
(c) having two types of nuclei.
(d) using pseudopodia for capturing prey.
4. Which of the following organisms are known as chief producers in the oceans? [2018]
(a) Dinoflagellates (b) Diatoms (c) Euglenoids (d) Cyanobacteria
5. After karyogamy followed by meiosis, spores are produced exogenously in __________. [2018]
(a) Neurospora (b) Alternaria (c) Saccharomyces (d) Agaricus
6. Which of the following components provides sticky character to the bacterial cell? [2017]
(a) Nuclear membrane (b) Plasma membrane (c) Glycocalyx (d) Cell wall
7. Which of the following are the smallest living cells, known without a definite cell wall, pathogenic to plants as well as animals and can survive without oxygen? [2017]
(a) Pseudomonas (b) Mycoplasma (c) Nostoc (d) Bacillus
8. Which of the following are found in extreme saline conditions? [2017]
(a) Eubacteria (b) Cyanobacteria (c) Mycobacteria (d) Archaebacteria
9. Viroids differ from viruses in having [2017]
(a) DNA molecules without protein coat. (b) RNA molecules with protein coat.
(c) RNA molecules without protein coat. (d) DNA molecules with protein coat.
10. Chrysophytes, euglenoids, dinoflagellates and slime moulds are included in which of the following kingdom? [2016]
(a) Monera (b) Protista (c) Fungi (d) Animalia
11. One of the major components of cell wall of most fungi is _________. [2016]
(a) chitin (b) peptidoglycan (c) cellulose (d) hemicellulose
12. Which one of the following statements is incorrect? [2016]
(a) Cyanobacteria are also called blue-green algae. (b) Golden algae are also called desmids.
(c) Eubacteria are also called false bacteria. (d) Phycomycetes are also called algal fungi.
13. Which of the following statements is incorrect for viroids? [2016]
(a) They lack a protein coat. (b) They are smaller than viruses.
(c) They cause infections. (d) Their RNA is of high molecular weight.
14. Which of the following structures is not found in a prokaryotic cell? [2015]
(a) Ribosome (b) Mesosome (c) Plasma membrane (d) Nuclear envelope
15. The structures that help some bacteria to attach to rocks and / or host tissues are : [2015]
(a) Fimbriae (b) Mesosomes (c) Holdfast (d) Rhizoids
16. Pick up the incorrect statement. [2015]
(a) Protista have photosynthetic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition.
(b) Some fungi are edible.
(c) Nuclear membrane is present in monera.
(d) Cell wall is absent in animalia.
17. In which group of organisms the cell walls form two thin overlapping shells which fit together?
[2015]
(a) Euglenoids (b) Dinoflagellates (c) Slime moulds (d) Chrysophytes
18. The imperfect fungi which are decomposer of litter and help in mineral cycling belong to : [2015]
(a) Basidiomycetes (b) Phycomycetes (c) Ascomycetes (d) Deuteromycetes
19. Which one is incorrect statement? [2015]
(a) Mucor has biflagellate zoospores.
(b) Haploid endosperm is a typical feature of gymnosperms.
(c) Brown algae have chlorophyll a and c and fucoxanthin.
(d) Archegonia are found in bryophyta, pteridophyta and gymnosperms.
20. Choose the incorrect statements. [2015]
(a) Neurospora is used in the study of biochemical genetics.
(b) Morels and truffles are poisonous mushrooms.
(c) Yeast is unicellular and useful in fermentation.
(d) Penicillium is multicellular and produces antibiotics.
21. Which one of the following matches is correct? [2015 ]
| a) | Alternaria | Sexual reproduction absent | Deuteromycetes |
| b) | Mucor | Reproduction by conjugation | Ascomycetes |
| c) | Agaricus | Parasitic fungus | Basidiomycetes |
| d) | Phytophthora | Aseptate mycelium | Basidiomycetes |
22. True nucleus is absent in _________. [2015]
(a) Mucor (b) Vaucheria (c) Volvox (d) Anabaena
23. Which of the following are most suitable indicators of SO2 pollution in the environment? [2015]
(a) Conifers (b) Algae (c) Fungi (d) Lichens
24. Viruses have [2014]
(a) DNA enclosed in a protein coat. (b) prokaryotic nucleus.
(c) single chromosome. (d) both DNA and RNA.
25. Five kingdom system of classification suggested by R.H.Whittaker is not based on [2014]
(a) presence or absence of a well-defined nucleus. (b) mode of reproduction.
(c) mode of nutrition. (d) complexity of body organisation.
26. Archaebacteria differ from eubacteria in : [2014]
(a) Cell membrane (b) Mode of nutrition (c) Cell shape (d) Mode of reproduction
27. The motile bacteria are able to move by : [2014]
(a) fimbriae (b) flagella (c) cilia (d) pili
28. Which one of the following fungi contains hallucinogens? [2014]
(a) Morchella esculenta (b) Amanita muscaria (c) Neurospora sp. (d) Ustilago sp.
29. Which of the following shows coiled RNA strand and capsomeres? [2014]
(a) Polio virus (b) Tobacco mosaic virus
(c) Measle virus (d) Retrovirus
30. Which of the following statements is incorrect? (NEET-2019)
(1) Viroids lack a protein coat (2) Viruses are obligate parasites
(3) Infective constituent in viruses is the protein coat
(4) Prions consist of abnormally folded proteins
31. Which of the following statements is incorrect? (NEET-2019)
(1) Morels and truffles are edible delicacies.
(2) Claviceps is a source of many alkaloids and LSD.
(3) Conidia are produced exogenously and ascospores endogenously.
(4) Yeasts have filamentous bodies with long thread-like hyphae.
32. Match Column – I with Column – II. (NEET-2019)
Column – I Column – II
(a) Saprophyte (i) Symbiotic association of fungi with plant roots
(b) Parasite (ii) Decomposition of dead organic materials
(c) Lichens (iii) Living on living plants or animals
(d) Mycorrhiza (iv) Symbiotic association of algae and fungi
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(1) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
(2) (iii) (ii) (i) (iv)
(3) (ii) (i) (iii) (iv)
(4) (ii) (iii) (iv) (i)
33. Mad cow disease in catttle is caused by an organism which has :- (NEET-2019 ODISSA)
(1) inert crystalline structure (2) abnormally folded protein
(3) free RNA without protein coat (4) free DNA without protein coat
34. Which of the following statements is correct ? (NEET-2019 ODISSA)
(1) Lichens do not grow in polluted areas.
(2) Algal component of lichens is called mycobiont.
(3) Fungal component of lichens is called phycobiont
(4) Lichens are not good pollution indicators.
35. Match the organisms in column-I with habitats in column-II (NEET-2019 ODISSA)
Column-I Column-II
(a) Halophiles (i) Hot springs
(b) Thermoacidophiles (ii) Aquatic environment
(c) Methanogens (iii) Guts of ruminants
(d) Cyanobacteria (iv) Salty area
Select the correct answer from the options given below :-
(1) (a)-(iv), (b)-(i), (c)-(iii), (d)-(ii) (2) (a)-(i), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iii), (d)-(iv)
(3) (a)-(iii), (b)-(iv), (c)-(ii), (d)-(i) (4) (a)-(ii), (b)-(iv), (c)-(iii), (d)-(i)
36. Which of the following is incorrect about Cynobacteria? (NEET-2020 COVID)
(1) They are photoautotrophs
(2) They lack heterocysts
(3) They often form blooms in polluted water bodies
(4) They have chlorophyll A similar to green plants
37. Which of the following is correct about viroids? (NEET-2020)
1) They have free DNA without protein coat
2) They have RNA with protein coat
3) They have free RNA without protein coat
4) They have DNA with protein coat
38. Which of the following statements is correct? [NEET-2021]
1) Fusion of protoplasms between two motile on non-motile gametes is called plasmogamy.
2) Organisms that depend on living plants are called saprophytes.
3) Some of the organisms can fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialized cells called sheath cells.
4) Fusion of two cells is called Karyogamy.
39. Given below are two statements: [NEET-2022]
Statement I: Mycoplasma can pass through less than 1 micron filter size.
Statement II: Mycoplasma are bacteria with cell wall.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
1) Both statements I and Statements II are correct
2) Both statement I and Statement II are incorrect
3) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
4) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
40. Which of the following is a correct statement? [NEET-2022]
1) Cyanobacteria area a group of autotrophic organisms classified under Kingdom Monera
2) Bacteria are exclusively heterotrophic organisms
3) Slime moulds are saprophytic organisms classified under Kingdom Monera
4) Mycoplasma have DNA, Ribosome and cell wall
NCERT LINE BY LINE QUESTIONS – ANSWERS
| 1) D | 2) D | 3) A | 4) D | 5) A | 6) D | 7) A | 8) A | 9) C | 10) B |
| 11) C | 12) D | 13) B | 14) A | 15) D | 16) B | 17) A | 18) A | 19) D | 20) A |
| 21) C | 22) B | 23) A | 24) D | 25) D | 26) A | 27) A | 28) C | 29) A | 30) D |
| 31) C | 32) C | 33) C | 34) B | 35) C | 36) A | 37) D | 38) A | 39) D | 40) D |
| 41) D | 42) A | 43) D | 44) D | 45) A | 46) A | 47) D | 48) A | 49) B | 50) A |
| 51) A | 52) A | 53) C | 54) C | 55) A | 56) A | 57) B | 58) A | 59) A | 60) D |
| 61) D | 62) A | 63) A | 64) B | 65) D | 66) C | 67) B | 68) C | 69) D | 70) C |
| 71) D | 72) D | 73) C | 74) C | 75) C | 76) C | 77) C | 78) A | 79) B | 80) C |
| 81) D | 82) C | 83) B | 84) D | 85) D | 86) D | 87) C | 88) A | 89) B | 90) C |
| 91) D | 92) B | 93) C | 94) B | 95) D | 96) D | 97) B | 98) A | 99) D | 100) C |
| 101) C | 102) C | 103) A | 104) A | 105) C | 106) B | 107) C | 108) C | 109) B | 110) C |
| 111) A | 112) B | 113) B | 114) C | 115) D | 116) C | 117) D | 118) A | 119) D | 120) C |
| 121) B | 122) A | 123) B | 124) C | 125) D | 126) D | 127) C | 128) D | 129) B | 130) C |
| 131) A | 132) B | 133) D | 134) D | 135) A | 136) B | 137) B | 138) D | 139) B | 140) B |
| 141) D | 142) A | 143) B | 144) B | 145) D | 146) B | 147) A | 148) B | 149) C | 150) A |
| 151)D | 152) D | 153) B | 154) A | 155) C | 156) D | 157) A |
NEET PREVIOUS YEARS QUESTIONS-ANSWERS
NEET PREVIOUS YEARS QUESTIONS-EXPLANATIONS
1. (d) Pseudopodia are locomotory structures in sarcodines (amoeboid).
2. (a) Saccharomyces i.e. yeast is an eukaryote (unicellular fungi). Mycobacterium is a bacterium.
Oscillatoria and Nostoc are cyanobacteria.
3. (c) Ciliates differs from other protozoans in having two types of nuclei. E.g., Paramoecium have two types of nuclei i.e. macronucleus & micronucleus.
4. (b) Diatoms are the chief producers or the most common form of phytoplankton in the ocean. They utilise inorganic nutrients to form proteins, fats and organic material & provide food for various sea creatures.
5. (d) In Agaricus (a genus of basidiomycetes), basidiospores or meiospores are produced exogenously. Neurospora (a genus of ascomycetes) produces ascospores as meiospores but endogenously inside the ascus). Alternaria (a genus of deuteromycetes) does not produce sexual spores. Saccharomyces (unicellular ascomycetes) produces ascospores, endogenously.
6. (c) Sticky character of the bacterial wall is due to glycocalyx which is rich in glycoproteins.
7. (b) Mycoplasmas are smallest, prokaryotes lacking cell wall and are pleomorphic in nature. These are pathogenic to both plants and animals.
8. (d) Archaebacteria are able to survive in harsh conditions due to the presence of branched lipid chain in cell membrane that reduces fluidity of cell membrane. It includes halophiles which are exclusively found in saline habitats.
9. (c) Viroids are sub-viral agents as infectious RNA particles, without protein coat.
10. (b) All unicellular eukaryotic organism like diatoms, desmids (chrysophytes), euglenoids, dinoflagellates
and slime mould are included in protista.
11. (a)
12. (c) Eubacteria are the true bacteria.
13. (d)
14. (d) Nuclear envelope is not found in a prokaryotic cell.
15. (a) Fimbriae help bacteria to get attachment with rocks or host body to get establishment and nutrition.
16. (c) The kingdom monera possesses unicellular organisms (e.g – bacteria) having no nuclear membrane.
17. (d) In chrysophytes, the cell walls form two thin overlapping shells held together. The body of diatoms
appears like soap box due to overlapping shells.
18. (d) Class-deuteromycetes contains imperfect fungi which play an important role in decomposition of
Organic wastes.
19. (a) The spores are non-motile in Mucor.
20. (b) Morel and truffles are used as food and they are members of ascomycetes fungi.
21. (a) Alternaria belongs to class – deuteromycetes, which lack sexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction
Takes place by conidia produced on conidiophores.
22. (d) Anabaena is a cyanobacteria which lack a true nucleus because of absence of nuclear membrane.
23. (d) Lichens cannot grow in the place where sulphur dioxide, pollutant is available in the environment.
24. (a)
25. (a)
26. (a) Archaebacteria differ from other bacteria in having a different cell wall structure. They lack
peptidoglyan in cell wall and possess a monolayer of branched fatty acids attached to glycerol by ether bonds in their cell membranes.
27. (b) Motile bacteria have thin filamentous extensions from their cell wall called flagella.
28. (b) Several mushrooms such as Amanita muscaria, Psilocybe mexicana and Panaeolus spp. secrete
hallucinogenic substances like psilocybin and psilocin.
These substances may destroy brain cells and perception power of human beings.
29. (b)
37. Viroids are infectious nucleic acid contains only ssRNA
38. Fusion of protoplasm between two motile or non – motile gametes is called plasmogamy
39 Mycoplasma are bacteria with out cell wall.
40. CYANOBACTERIA comes under KINGDOM Monera
