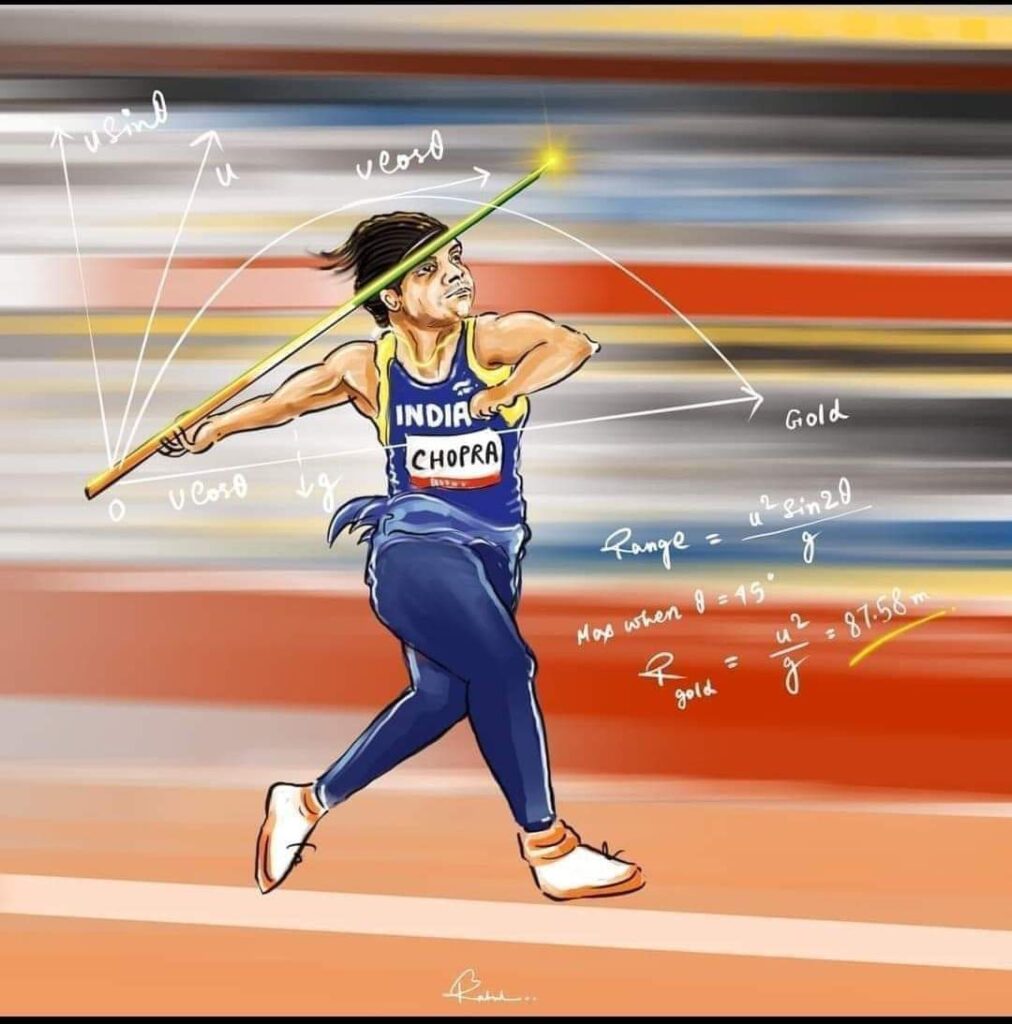
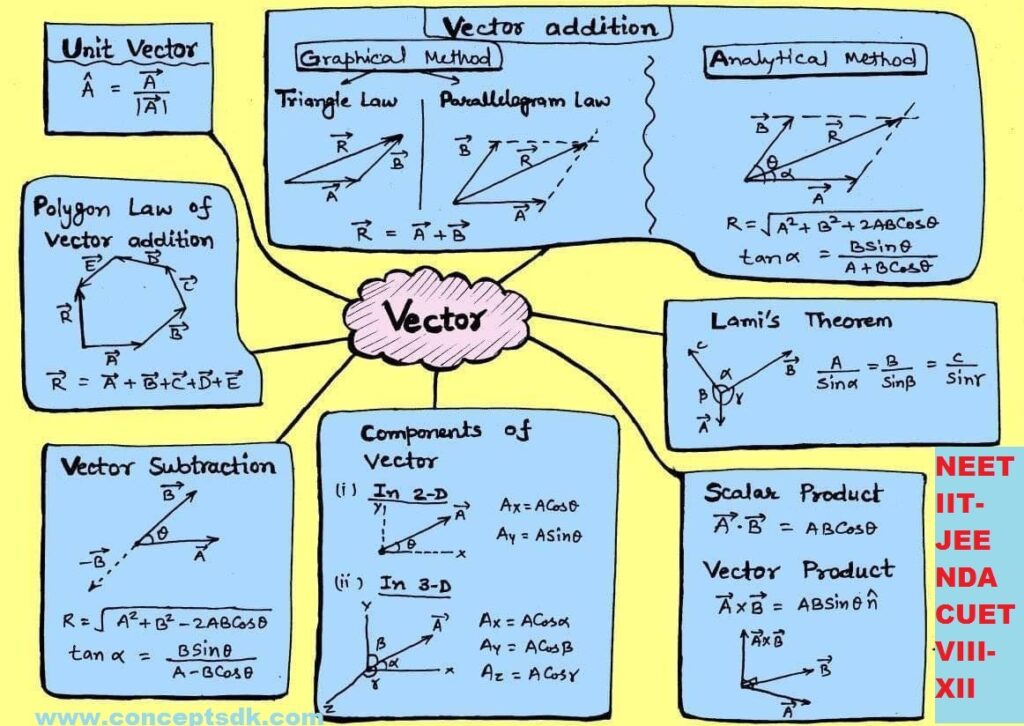
Syllabus:– Scalar and vector quantities; Position and displacement vectors, general vectors and their notations; equality of vectors, multiplication of vectors by a real number; addition and subtraction of vectors. Relative velocity. Unit vector; Resolution of a vector in a plane – rectangular components. Scalar and Vector product of vectors. Motion in a plane, cases of uniform velocity and uniform acceleration-projectile motion. Uniform circular motion.
REVISION NOTES






MCQ
Q. 1 For an object thrown at 45° to the horizontal, the maximum height (H) and horizontal range (R) are related as
(a) R = 16 H (b) R = 8 H (c) R = 4 H (d) R = 2 H
Q.2 At the upper most of a projectile, its velocity and acceleration at an angle of
(a) 0° (b) 45° (c) 90° (d) 180°
Q.3 The x and y coordinates of a particle at any time t is given by x = 7t + 4t2 and y = 5t, where x and y are in metre and t in seconds. The acceleration of particle at t = 5s is
(a) Zero (b) 8 m/s2 (c) 20 m/s2 (d) 40 m/s2
Q.4 A body projected at an angle with the horizontal has a range 300 m. The time of flight is 6s, then the horizontal component of velocity is
(a) 30 m/s (b) 50 m/s (c) 40 m/s (d) 45 m/s
Q.5 A projectile rises to a height of 10 m and then falls at a distance of 30 m away from the projection. Its vertical displacement is
(a) 0 m (b) 5 m (c) 6 m (d) 7 m
Answers
- C
- C
- B
- B
- A
QUESTION BANK
- Under what condition is the average velocity equal the instantaneous
velocity ? - Draw Position time graph of two objects, A & B moving along a straight line, when their relative velocity is zero.
- Suggest a situation in which an object is accelerated and have constant speed.
- Two balls of different masses are thrown vertically upward with same initial velocity. Maximum heights attained by them are h1 and h2 respectively what is h1/h2 ?
- A car moving with velocity of 50 kmh–1 on a straight road is ahead of a jeep moving with velocity 75 kmh–1 . How would the relative velocity be altered if jeep is ahead of car ?
- Which of the two-linear velocity or the linear acceleration gives the direction of motion of a body ?
- Will the displacement of a particle change on changing the position of origin of the coordinate system ?
- If the instantaneous velocity of a particle is zero, will its instantaneous
acceleration be necessarily zero ? - What is the maximum number of component into which a vector can be resolved ?
- A body projected horizontally moves with the same horizontal velocity although it moves under gravity. Why ?
- What is the angle between velocity and acceleration at the highest point of
a projectile motion ? - When does (i) height attained by a projectile maximum ? (ii) horizontal
range is maximum ? - What is the angle between velocity vector and acceleration vector in
uniform circular motion ? - A particle is in clockwise uniform circular motion the direction of its acceleration is radially inward. If sense of rotation or particle is anticlockwise then what is the direction of its acceleration ?
- A train is moving on a straight track with acceleration a. A passenger drops
a stone. What is the acceleration of stone with respect to passenger ? - What is the average value of acceleration vector in uniform circular motion
over one cycle ? - Does a vector quantity depends upon frame of reference chosen ?
- What is the angular velocity of the hour hand of a clock ?
- What is the source of centripetal acceleration for earth to go round the
sun ?
Numerical
- The V-t graphs of two objects make angle 30° and 60° with the time axis.
Find the ratio of their accelerations. - When the angle between two vectors of equal magnitudes is 2π/3, prove that the magnitude of the resultant is equal to either.
- On a 60 km straight road, a bus travels the first 30 km with a uniform speed of 30 kmh–1 . How fast must the bus travel the next 30 km so as to have average speed of 40 kmh–1 for the entire trip ?The displacement x of a particle varies with time as x = 4t2 – 15t + 25. Find the position, velocity and acceleration of the particle at t = 0.
- A driver take 0.20 second to apply the breaks (reaction time). If he is driving car at a speed of 54 kmh–1 and the breaks cause a decleration of 6.0 ms–2. Find the distance travelled by car after he sees the need to put the breaks.
- From the top of a tower 100 m in height a ball is dropped and at the same time another ball is projected vertically upwards from the ground with a velocity of 25 m/s. Find when and where the two balls will meet ? (g = 9.8 m/s2)
- A ball thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 19.6 ms–1 from the top of a tower returns to the earth in 6s. Find the height of the tower. (g = 9.8 m/ s2)
- Two town A and B are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A man cycling with a speed of 20 kmh–1 in the direction A to B notices that a bus goes past him every 18 min in the direction of his motion, and every 6 min in the opposite direction. What is the period T of the bus service and with what speed do the busses ply of the road ?
- A motorboat is racing towards north at 25 kmh–1 and the water current in that region is 10 kmh–1 in the direction of 60° east of south. Find the resultant velocity of the boat.
- A hiker stands on the edge of a clift 490 m above the ground and throws a stone horizontally with an initial speed of 15 ms–1. Neglecting air resistance, find the time taken by the stone to reach the ground and the speed with which it hits the ground. (g = 9.8 ms–2)
- A bullet fired at an angle of 30° with the horizontal hits the ground 3 km away. By adjusting the angle of projection, can one hope to hit the target 5 km away ? Assume that the muzzle speed to be fixed and neglect air resistance.
- A stone tied to the end of a string 80 cm long is whirled in a horizontal circle with a constant speed. If the stone makes 14 revolutions in 25 seconds, what is the magnitude and direction of acceleration of the stone ?
- A cyclist is riding with a speed of 27 kmh–1 . As he approaches a circular turn on the road of radius 30 m, he applies brakes and reduces his speed at the constant rate 0.5 ms–2. What is the magnitude and direction of the net acceleration of the cyclist on the circular turn ?

