- What is the role of NAD+ in cellular respiration? [2018]
(a) It functions as an enzyme.
(b) It functions as an electron carrier.
(c) It is the final electron acceptor for anaerobic respiration.
(d) It is a nucleotide source for ATP synthesis.
2. Which of these statements is incorrect? [2018]
(a) Enzymes of TCA cycle are present in mitochondrial matrix.
(b) Glycolysis occurs in cytosol.
(c) Oxidative phosphorylation takes place in outer mitochondrial membrane.
(d) Glycolysis operates as long as it is supplied with NAD that can pick up hydrogen atoms.
3. Phosphoenol Pyruvate (PEP) is the primary CO2 acceptor in __________. [2017]
(a) C4 plants (b) C2 plants (c) C3 and C4 plants (d) C3 plants
4. Which statement is wrong for Krebs’ cycle? [2017]
(a) There is one point in the cycle where FAD+ is reduced to FADH2.
(b) During conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid, a molecule of GTP is synthesised.
(c) The cycle starts with condensation of acetyl group (acetyl CoA) with pyruvic acid to yield citric acid.
(d) There are three points in the cycle where NAD+ is reduced to NADH + H+.
5. In which one of the following processes CO2 in not released? [2014]
(a) Aerobic respiration in plants. (b) Aerobic respiration in animals.
(c) Alcoholic fermentation. (d) Lactate fermentation.
6. Respiratory Quotient (RQ) value of tripalmitin is : [NEET-2019]
(1) 0.9 (2) 0.7 (3) 0.07 (4) 0.09
7. Conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate, the first irreversible reaction of glycolysis, is catalyzed by [NEET-2019]
(1) Aldolase (2) Hexokinase
(3) Enolase (4) Phosphofructokinase
8. Where is respiratory electron transport system (ETS) located in plants ? [NEET-2019 ODISSA]
(1) Mitochondrial matrix (2) Outer mitochondrial membrane
(3) Inner mitochondrial membrane (4) Intermembrane space
9. Pyruvate dehydrogenase activity during aerobic respiration requires [NEET-2020 COVID]
(1) Calcium (2) Iron (3) Cobalt (4) Magnesium
10. The number of substrate level phosphorylations in one turn of citric acid cycle is [NEET-2020]
1) Three 2) Zero 3) One 4) Two
11. Which of the following statements is incorrect? [NEET-2021]
1) In ETC (Electron Transport Chain), one molecule of NADH+H+ gives rise to 2 ATP molecules, and one FADH2 gives rise to 3 ATP molecules.
2) ATP is synthesized through complex V.
3) Oxidation-reduction reactions produce proton gradient in respiration.
4) During aerobic respiration, role of oxygen is limited to the terminal stage.
12. What amount of energy is released from glucose during lactic acid fermentation?
1) Approximately 15% 2) More than 18%
3) About 10% 4) Less than 7%
13. What is the net gain of ATP when each molecule of glucose is converted to two molecules of pyruvic acid?
1) Four 2) Six 3) Two 4) Eight
NEET PREVIOUS YEARS QUESTIONS-ANSWERS
1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (a) 4 (c) 5 (d) 6 (2) 7 (2) 8 (3) 9 (4) 10 (3)
11 (1) 12 (4) 13 (3)
NEET PREVIOUS YEARS QUESTIONS-EXPLANATIONS
1. (b) In cellular respiration, NAD+ act as an electron carrier.
2. (c) Oxidative phosphorylation takes place in inner mitochondrial membrane.
3. (a) In the mesophyll cells cytoplasm of C4 plants like sugarcane, maize, sorghum etc. PEP is 3C
Compound which serves as primary CO2 acceptor.
4. (c) Krebs cycle begins with condensation of acetyl CoA (2C) with oxaloacetic acid (4C) to form citric acid (6C).
5. (d) Lactic acid fermentation: It occurs in lactic acid bacteria (Lactobacillus) and muscles (Human). Pyruvic acid produced in glycolysis is reduced by NADH2 to form lactic acid without producing carbon dioxide.
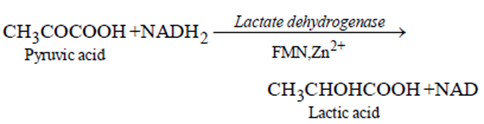
10. In citric acid cycle during conversation of succinyl succinic acid, one ATP molecule is synthesized by substrate level phosphorylations
11. In ETC –
1 NADH – 3 ATP ; 1 FADH2 – 2 ATP
12. Lactic acid fermentation – less than 7%
13. In glycolysis the net gain of ATP is 2
