Motion: The action or process of moving or being moved.
The distance moved by an object in a unit time is called its speed.
Speed of objects help us to decide which one is moving faster than the other.
The speed of an object is the distance travelled divided by the time taken to cover that distance. Its basic unit is metre per second (m/s).
Periodic events are used for the measurement of time. Periodic motion of a pendulum has been used to make clocks and watches.
Motion of objects can be presented in pictorial form by their distance-time graphs.
The distance-time graph for the motion of an object moving with a constant speed is a straight line.
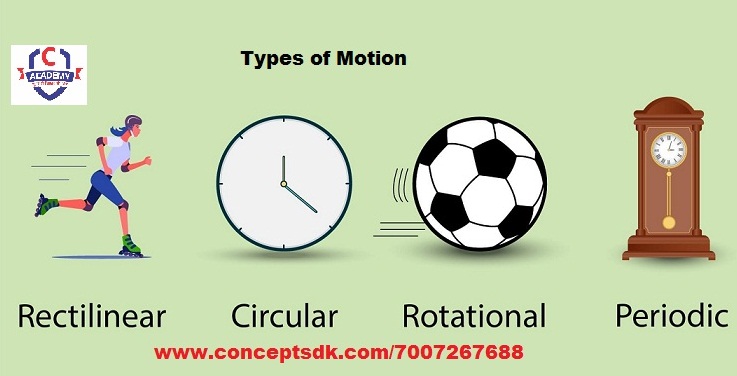
Types of Motion:
(i) Uniform motion: An object moving along a straight line with a constant speed is said to be in uniform motion. The average speed is the same as the actual speed.
(ii) Non-Uniform motion: If the speed of an object moving along a straight line keeps changing, its motion is said to be non-uniform.
Speed: It is the distance covered by an object in a unit time. Basic unit of speed is m/s.
Speed = Distance/Time
Average Speed: It is the total distance covered by an object in a total time. Basic unit of speed is m/s.
Average Speed = Total Distance / Total Time
Distance-Time Graph: Motion of objects can be presented in pictorial form by their distance-time graphs. The distance-time graph for the motion of an object moving with a constant speed is a straight line.