

REVISION CONCEPTS
A stream of electrons moving through a conductor constitutes an electric current. Conventionally, the direction of current is taken opposite to the direction of flow of electrons.
The SI unit of electric current is ampere.
To set the electrons in motion in an electric circuit, we use a cell or a battery. A cell generates a potential difference across its terminals. It is measured in volts (V).
Resistance is a property that resists the flow of electrons in a conductor. It controls the magnitude of the current. The SI unit of resistance is ohm (Ω ).
Ohm’s law: The potential difference across the ends of a resistor is directly proportional to the current through it, provided its temperature remains the same.
The resistance of a conductor depends directly on its length, inversely on its area of cross-section, and also on the material of the conductor.
The equivalent resistance of several resistors in series is equal to the sum of their individual resistances.
A set of resistors connected in parallel has an equivalent resistance Rp given by
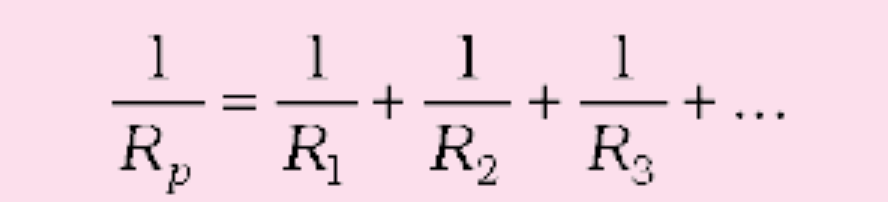
The electrical energy dissipated in a resistor is given by
W = V × I × t
The unit of power is watt (W). One watt of power is consumed when 1 A of current flows at a potential difference of 1 V.
The commercial unit of electrical energy is kilowatt hour (kWh).
1 kW h = 3,600,000 J = 3.6 × 10^6 J.
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
Question:- What does an electric circuit mean?
Answer. A continuous conducting path consisting of wires and other resistances and a switch between the two terminals of a cell or a battery along which an electric current flow is called a circuit
Question:- Explain the following:
(a) Why the tungsten a used almost exclusively for the filament of electric lamps?
Answer. It has a special property that it glows on heating.
It has ,i high melting point.
It does not tenet with the gases present in air and does not get oxidized.
It has a low resistance.
(b) Why are the conductors of electric heating devices, such as bread-toasters and electric irons, made up of alloys rather than a pure menu?
Answer:- They offer higher resistance than pure metals, thus heating better.
They have a high melting point.
They do not oxidize.
(c) Why is the series arrangement not used for domestic circuits?
Answer:-If any appliance is at fault, then the current is not able to flow through.
Different appliances have different current requirements, but in series the current is the same. This can cause a power surge, thus damaging the appliances.
Very long wires m domestic series circuits offer unusually high resistance, which is unwanted. (d) How does the resistance of a wire vary with its area of cross section?
Answer:- Directly proportional.
(e) Why copper and aluminium wires are usually employed for electricity transmission?
Answer:- Copper and aluminium are much more easily and cheaply available than other metals. They offer low resistance and do not get heated.
They can be easily made into wires due to high malleability.
Question :- What are the advantages of connecting electrical devices in parallel with the battery instead of connecting them in series?
Answer:- Advantages of parallel connection are:In parallel circuit, if one electric appliance stop working due to some defect, then all other appliances keep working normally.
In parallel circuit, each electrical appliance has its own switch due to which they can be turned on or off without affecting other appliances.
Each electrical appliance get the same voltage (220 V) as that of the power supply line.
In parallel connection of electrical appliances, the overall resistance of the circuit is reduced due to which the current from the power supply is high.
Question:- Why are coils of electric toasters and electric irons made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
Answer:- The coils of such heating appliances are made up of an alloy rather than a pure metal because:
(a) The resistivity of an alloy is much higher than that of a pure metal.
(b) An alloy does not undergo oxidation easily even at high temperature when it is even red hot.
Question:- Will current flow more easily through a thick wire or a thin wire of the same material, when connected to the same source? Why?
Answer:- The current will flow more easily through a thick wire as compared to the thin wire because the resistance of thick wire is less than that of thin wire. Less resistance, means more current.
Question:- Define the unit of current or Define 1 Ampere.
Ans. The unit of current is Ampere. 1 Ampere is said to be when 1 coulomb of charge flow through any cross section of a conductor in 1 second.

