Questions based on Direct NCERT and NEET PYQs.
1. Amphibians e.g. frogs respire –
(A) Through moist skin (B) Lungs
(C) Both a and b (D) Trachea
2. Which is correct about nasopharynx?
(A) Internal nostrils open into nasopharynx
(B) It is the common passage for both air and food
(C) It opens through gullet of the larynx region into the trachea
(D) All
3. Which of the following options is wrong about the larynx (sound box)?
(A) It is a bony box
(B) Glottis is the opening into the larynx
(C) During swallowing of food glottis is covered by epiglottis to prevent food entry into the larynx
(D) All
4. Trachea divides into right and left primary bronchi at _ thoracic vertebra.
(A) 4 (B) 5 (C) 6 (D) 9
5. Incomplete cartilaginous rings support all of the following except-
(A) Trachea
(B) Primary, secondary and tertiary bronchi
(C) Respiratory bronchioles
(D) Initial bronchioles
6. Which of the following has the smallest diameter?
(A) Trachea
(B) Terminal bronchiole
(C) Tertiary bronchus
(D) Secondary bronchus
7. Expiration takes place when the intrapulmonary pressure is –
(A) Greater than the atmospheric pressure
(B) Lesser than the atmospheric pressure
(C) Equal to atmospheric pressure
(D) Equal to intrapleural pressure
8. Which of the following sequences is correct to initiate inspiration?
I. The contraction of external intercostal muscles raises the ribs and sternum
II. Volume of thorax increases in the dorso-ventral axis
III. Intrapulmonary pressure Decreases
IV. Diaphragm contraction
V. Air rushes into lungs
VI. Volume of thorax increases in the anterio-posterior axis
(A) I, II, IV, V, III, VI (B) I, II, III, IV, V
(C) I, II, IV, VI, III, V (D) VI, I, II, III, V
9. Following illustration depicts the mechanism of breathing. In which of the following option all the parts A. B, C and D are correctly labelled?
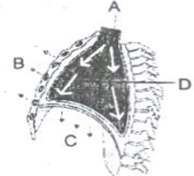
(A) A-Air entering into lungs; B- Ribs and sternum raised; C- Diaphragm contracted; D-Volume of thorax raised
(B) A – Air expelled from lungs; B – Ribs and sternum return to original position; C – Diaphragm relaxed; D – Volume of thorax decreased
(C) A-Air expelled from lungs; B- Ribs and sternum raised; C – Diaphragm relaxed; D -Volume of thorax decreased
(D) A-Air expelled from lungs; B- Ribs and sternum raised; C- Diaphragm contracted; D-Volume of thorax decreased
10. Emphysema is characterised by –
(A)Permanent enlargement and destruction of alveolar area leading to reduction in respiratory surface
(B) Inhibition of respiratory centre
(C) Accumulation of fluid in lungs
(D) Spasm of muscles of trachea
11. The partial pressure of CO2 in the venous blood is –
(A) Greater than in the tissue spaces
(B) Lesser than in the tissue spaces
(C) Lesser than in the arterial blood
(D) Less than in alveoli
12. Besides RBC blood plasma also carries O2 in solution. The percentage is
(A) 3% (B) 97% (C) 49% (D) 25%
13. The majority of CO2 is transported as –
(A) Carbonates
(B) Bicarbonates
(C) Carbaminohaemoglobin
(D) Dissolved state in blood
14. Dissociation curve is associated with –
(A) Carbonic anhydrase (B) CO
(C) CHCl3 (D) Oxyhemoglobin
15. Binding of O2 with hemoglobin is primarily related to-
(A) pO2 (B) pCO2
(C) H+ conc. (D) None
16. Besides pO2 the other factor(s) affecting the binding of O2 with hemoglobin is/are
(A) pCO2 (B) H+ nk.
(C) Temperature (D)All
17. Oxygen dissociation curve is –
(A) J-shaped (B) S-shaped
(C) L-shaped (D) Zig-zag
18. The breathing centre initiates ventilation in response to –
(A) A decrease in air pressure
(B)A decrease in O2
(C) An increase in CO2
(D) The rate of gas exchange in the alveoli
19. All of the following factors play role in the regulation of respiratory rhythm except –
(A) CO2 (B) H+ conc.
(C) O2 (D) None of the above
20. Asthma is caused by –
(A) Infections of lungs
(B) Infection of trachea
(C) Spasm in bronchial muscles
(D) Infection in nose
21. One reason for emphysema is –
(A) Cigarette smoking
(B) Drug addiction
(C) Wine consumption
(D) Heavy exercise
22. Emphysema is characterised by –
(A) Permanent enlargement and destruction of alveolar area leading to reduction in respiratory surface
(B) Inhibition of respiratory centre
(C) Accumulation of fluid in lungs
(D) Spasm of muscles of trachea
23. Why do human beings have difficulty breathing at high elevations?
(A) O2 makes up lower percentage of air there
(B) The temperature is lower there
(C) The barometric pressure is higher there
(D) pO2 is lower there
24. Lungs are made up of air-filled sacs, the alveoli. They do not collapse even after forceful expiration, because of
(a) inspiratory reserve volume.
(b) tidal volume.
(c) expiratory reserve volume.
(d) residual volume.
25. Name the chronic respiratory disorder caused mainly by cigarette smoking.
(a) Emphysema
(b) Asthma
(c) Respiratory acidosis
(d) Respiratory alkalosis
26. Due to increasing air-borne allergens and pollutants, many people in urban areas are suffering from respiratory disorder causing wheezing due to :
(1) benign growth on mucous lining of nasal cavity.
(2) inflammation of bronchi and bronchioles.
(3) proliferation of fibrous tissues and damage of the alveolar walls.
(4) reduction in the secretion of surfactants by pneumocytes
27. Select the correct statement.
(1) Expiration occurs due to external intercostal muscles
(2) Intrapulmonary pressure is lower than the atmospheric pressure during inspiration.
(3) Inspiration occurs when atmospheric pressure is less than intrapulmonary pressure.
(4) Expiration is initiated due to contraction of diaphragm.
28. The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration is known as :
(1) Expiratory Capacity
(2) Vital Capacity
(3) Inspiratory Capacity
(4) Total lung Capacity
29. Identify the wrong statement with reference to transport of oxygen
1) Low pCO2 in alveoli favours the formation of oxyhaemoglobin
2) Binding of oxygen with haemoglobin is mainly related to partial pressure of O2.
3) Partial pressure of CO2 can interfere with O2 binding with haemoglobin
4) Higher H+ conc. in alveoli favours the formation of oxyhaemoglobin
30. The inner alveolar surface area of lungs is
(A) 10 m² (B) 90 m²
(C) 250 m² (D) 600 m²
31. The volume of air inspired or expired during normal respiration is called
(A) Inspiratory capacity
(B) Tidal volume
(C) Inspiratory reserve volume
(D) Vital capacity
32. A spirometer can be used to directly measure
(A) Residual volume
(B) Vital capacity
(C) Functional residual capacity
(D) Total lung capacity
33. Identify the wrong statement:
(A) Phrenic muscles are present in diaphragm.
(B) During inspiration, diaphragm contracts and becomes dome shaped.
(C) Vital capacity is higher in males than in females.
(D) Residual volume is present in our lungs after forceful expiration.
34. The lowest mechanical efforts are required in the respiration of
(A) Vital capacity
(B) Expiratory reserve volume
(C) Inspiratory reserve volume
(D) Tidal volume
35. Which of the following event is observed during normal expiration?
(A) Contraction of diaphragm
(B) Contraction of external intercostal muscles
(C) Relaxation of diaphragm
(D) Rise in the volume of thoracic cavity
36. Match the following
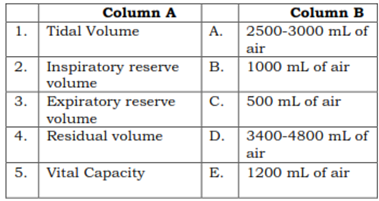
(A) 1 – C, 2 – D, 3 – B, 4 – A, 5 – E
(B) 1 – C, 2 -A, 3 – B, 4 – E, 5 – D
(C) 1 – C, 2 -A, 3 – D, 4 – E, 5 – B
(D) 1 – E, 2 -A, 3 – B, 4 – E, 5 – D
37. Name the blood vessels A to D
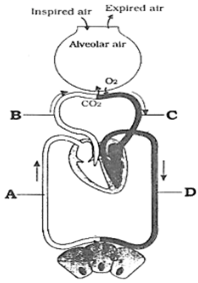
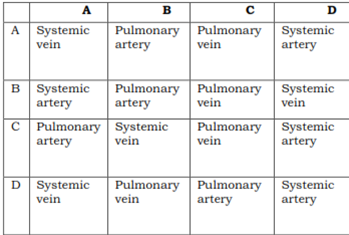
Answer A
38. Study the given figure and identify A to C.
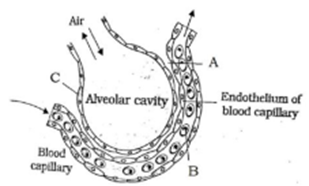
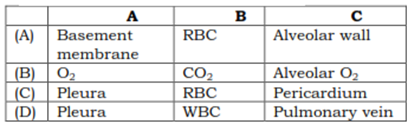
Answer A
39. Which of the following would have the same O2 content?
(A) Blood entering the lungs – blood leaving the lungs
(B) Blood entering the right side of the heart – blood leaving the right side of the heart
(C) Blood entering the right side of the heart- blood leaving the left side of the heart
(D) Blood entering the tissue capillaries – blood leaving the tissue capillaries
40. Assertion – A drop in the blood pH causes an increase in heart rate.
Reason- Increased Heart Rate increases the rate at which CO2 is delivered to the lungs, where CO2 is removed.
A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
B) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
C) Assertion is true but reason is false.
D) Both assertion and reason are false.
41. Assertion- The maximum pO2 in alveoli is considerably less than in the atmosphere.
Reason- Lungs in mammals do not completely empty with each breath and inhalation occurs through the same airways as exhalation, so each inhalation mixes fresh air with oxygen depleted residual air.
A) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
B) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
C) Assertion is true but reason is false.
D) Both assertion and reason are false.
42. Match the items given in column I with those in column II and select the correct option given below:
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Tidal volume | I. 2500 – 3000 mL |
| B. Inspiratory Reserve volume | II. 1100 – 1200 mL |
| C. Expiratory Reserve volume | III. 500 – 550 mL |
| D. Residual volume | IV. 1000 – 1100 mL |
(a) A – III; B – II; C – I; D – IV
(b) A – III; B – I; C –IV; D – II
(c) A – IV; B – III; C – II; D – I
(d) A – I; B – IV; C – II; D – III
43. Select the correct statement. (NEET-2019 ODISSA)
(1) Expiration occurs due to external intercostal muscles
(2) Intrapulmonary pressure is lower than the atmospheric pressure during inspiration.
(3) Inspiration occurs when atmospheric pressure is less than intrapulmonary pressure.
(4) Expiration is initiated due to contraction of diaphragm.
44. Match the following columns and select the correct option :
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Pneumotaxic | (i) Alveoli Centre |
| (b) O2 Dissociation | (ii) Pons region of curve brain |
| (c) Carbonic | (iii) Haemoglobin Anhydrase |
| (d) Primary site | (iv) R.B.C. of exchange of gases |
(1) (a)-(i), (b)-(iii), (c)-(ii), (d)-(iv)
(2) (a)-(ii), (b)-(iii), (c)-(iv), (d)-(i)
(3) (a)-(iii), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iv), (d)-(i)
(4) (a)-(iv), (b)-(i), (c)-(iii), (d)-(ii)
45. Identify the wrong statement with reference to transport of oxygen (NEET-2020)
1) Low pCO2 in alveoli favours the formation of oxyhaemoglobin
2) Binding of oxygen with haemoglobin is mainly related to partial pressure of O2.
3) Partial pressure of CO2 can interfere with O2 binding with haemoglobin
4) Higher H+ conc. in alveoli favours the formation of oxyhaemoglobin
46. Select the correct events that occur during inspiration (NEET-2020)
a) Contraction of diaphragm
b) Contraction of external inter-costal muscles
c) Pulmonary volume decreases
d) Intra pulmonary pressure increases
1) Only (d) 2) (a) and (b)
3) (c) and (d) 4) (a), (b) and (d)
47. Which of the following is not the function of conducting part of respiratory system?
1) It clears inhaled air from foreign particles
2) Inhaled air is humidified
3) Temperature of inhaled air is brought to body temperature
4) Provides surface for diffusion of O2 and CO2
48. Antennal glands or green glands are the respiratory organs of
(A) Echinoderms
(B) Crustaceans like prawns
(C) Insects like cockroach
(D) Planarians
49. Which of the following part of the respiratory tract does not have cartilaginous rings in its wall?
(A) Trachea
(B) Primary bronchi
(C) Secondary bronchi
(D) Respiratory bronchiole
50. All of the following form conducting part of the respiratory tract, except
(A) Trachea
(B) Secondary bronchi
(C) Respiratory bronchiole
(D) Terminal bronchiole
