Paragraph 6.1 The Tissues
Paragraph 6.1.1 Meristematic tissues:
1. Apical meristems (Pg. 84, E)
A) Occur at root tip B) Produce primary tissues
C) Regenerate parts of plant D) Both A & B
2. During leaf formation and stem elongation, some cells of apical meristem left behind form-
(Pg. 84, E)
A) Primary cell. B) Intercalary meristem
C) Axillary bud D) Interfascicular cambium
3. Intercalary meristem (Pg. 85, E)
A) Occur in grasses B) Occur between mature tissue
C) Both A & B D) None
4. Primary meristem (Pg. 85, E)
A) Appear later in life of plant B) Appear early in life of plant
C) Regenerates parts of plant D) Both B & C
5. Primary body of plant is formed by- (Pg. 85, E)
A) Meristem B) Vascular cambium
C) Both A & B D) None
6. Lateral meristem are- (Pg. 85, E)
A) Type of primary meristem
B) Appearing early in life of plant
C) Responsible for producing secondary tissues
D) Both A & B
7. Secondary meristem include- (Pg. 85, E)
A) Fascicular vascular cambium B) Cork cambium
C) Secondary phloem D) Both A and B
8. Meristem that occur in mature region of root and shoot of plant- (Pg. 85, E)
A) Apical meristem B) Intercalary meristem
C) Lateral meristem D) None of these
9. Identify the correct labels- (Pg. 85, E)
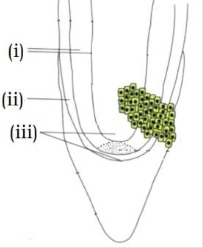
A) (i) – cortex, (ii) – Protoderm, (iii) –initial of central cylinder & cortex
B) (i) – Protoderm, (ii) – cortex, (iii) – central cylinder
C) (i) – central cylinder, (ii) – cortex, (iii) – Protoderm
D) (i) – central cylinder, (ii) – Protodrem, (iii) – cortex
10. Identify the axillary bud in given figure – (Pg. 85, E)
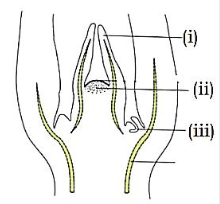
A) (i) B) (ii) C) (iii) D) Both (ii) and (iii)
Paragraph – 6.1.2 Permanent
Tissue
11. Cell of permanent tissue (Pg. 86, E)
A) Divide regularly to repair damage B) Divide occasionally
C) Do not divide generally D) Both (B) and (C)
12. Simple tissue are – (Pg. 86, E)
A) Meristematic tissues having all cells similar in structure and function
B) Meristematic tissues having different types of cells
C) Permanent tissues having all cells similar in structure and function
D) Permanent tissues having many different type of cells
13. Complex tissues are – (Pg. 86, E)
A) Meristematic tissues having all cells similar in structure and function
B) Permanent tissues having all cells similar in structure and function
C) Meristematic tissues having different types of cells
D) Permanent tissues having different types of cells.
Paragraph – 6.1.2.1 Simple tissue
14. Simple tissues are made of (Pg. 86, E)
A) Some types of cells of similar origin
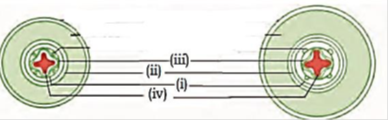
B) Only one type cells
C) Different types of cells of same origin
D) Different types of cells of different origin
15. Major component within organs is formed by – (Pg. 86, E)
A) Collenchyma B) Sclerenchyma
C) Parenchyma D) All of these
16. Walls of parenchyma are made of– (Pg. 86, E)
A) Proteose B) Cellulose C) Keratin D) Pectin
17. Parenchyma performs functions – (Pg. 86, E)
A) Photosynthesis B) Storage
C) Secretion D) All of the above
18. Parenchyma cells are generally – (Pg. 86, E)
A) Of varying diameters, with no intercellular space
B) Of similar diameters, with no intercellular space
C) Of similar diameters, with small intercellular space
D) Both B and C
19. Where does collenchyma occur? (Pg. 86, E)
A) Below endodermis in most monocots
B) Below epidermis in most monocots
C) Below epidermis in most dicots
D) Below endodermis in most dicots
20. Cell of collenchyma are thickened at corners due to deposition of (Pg. 86, E)
A) Cellulose B) Hemicellulose
C) Pectin D) All of these
21. Collenchyma cells – (Pg. 86, E)
A) May be polygonal and never contain chloroplasts.
B) May be polygonal and often contain chloroplasts
C) May be oval and contain chloroplasts
D) Both B and C
22. Collenchyma cells (Pg. 86, E)
A) Have no intercellular spaces
B) Have large intercellular spaces
C) May or may not have intercellular spaces
D) None of these
23. Mechanical support in plants is provides by (Pg. 86, E)
A) Parenchyma B) Collenchyma
C) Sclerenchyma D) Both B and C
24. Choose the best option (Pg. 86, M)
A) All collenchymatous cells Assimilate food
B) No collenchymatous cells assimilate food
C) Some collenchymatous cells do not assimilate food
D) All collenchymatous cells do not assimilate food
25. Collenchyma provide mechanical support to – (Pg. 86, E)
A) Young stem B) Petiole of leaf organs only
C) Organs only D) All of these
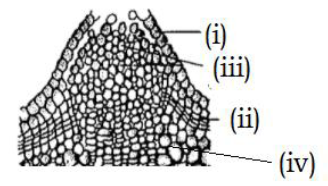
26. Identify the given figure (Pg. 86, E)
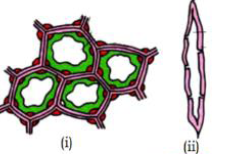
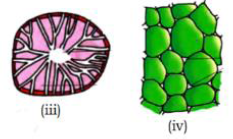
A) (i) – parenchyma, (ii) – fibre, (iii) – sclereid, (iv) – collenchyma
B) (i) – sclereids, (ii) – fibre, (iii) – parenchyma, (iv) collenchyma
C) (i) – collenchyma, (ii) – sclerids, (iii) – fobres, (iv) – parenchyma
D) (i) – collenchyma, (ii) fibre, (iii) – sclereids, (iv) – parenchyma
27. Sclenenchyma cells are – (Pg. 86, E)
A) Usually dead with protoplast B) Usually dead without protoplast
C) Usually living with protoplast D) Usually living without protoplast
28. Read the given statements – (Pg. 86, M)
(i) Sclereids are found in leaves of tea.
(ii) Fibres generally occur single in various plant parts.
(iii) Sclerenchyma provides mechanical support to young stems.
(iv) Parenchyma cells have thick walls.
(v) Collenchyma cells are thickened at corners.
How many are correct
A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 1
29. Pulp of pear has which type of sclerenchyma cells- (Pg. 87, E)
A) Sclereids B) Fibres C) Tracheids D) Trichomes
Paragraph – 6.1.2.2
Complex Tissues
30. Complex tissues are – (Pg. 87, E)
A) Made of one of cells, working as unit
B) Made of many types of cells, working as a unit
C) Made of one type of cells, working separately
D) Made of many types of cells, working separately
31. Xylem has following functions except– (Pg. 87, E)
A) Conducting water from roots to upper plant part
B) Conducting minerals from leaves to roots
C) Providing mechanical strength to plant parts
D) Conducting sap from roots to leaves
32. Xylem tissue consists of- (Pg. 87, E)
A) Sieve tube, companion cells, fibres, parenchyma
B) Sieve cells, vessels, fibres, parenchyma
C) Vessels, tracheids, sieve tube, fibres
D) Vessels, tracheid, fibres, parenchyma
33. Gymnosperms lack- (Pg. 87, E)
A) Xylem vessels B) Companion cells
C) Sieve tubes and companion cells D) All of the above
34. Phloem of gymnosperms possess- (Pg. 87, E)
A) Albuminous cells B) Companion cells
C) Sieve tube D) Both (B) and (C)
35. Xylem has all dead cells except- (Pg. 87, E)
A) Xylem parenchyma B) Xylem fibres
C) Xylem vessels D) Xylem tracheids
36. Ray parenchymatous cells help in – (Pg. 87, E)
A) Radial conduction of food B) Axial conduction of water
C) Axial conduction of food D) Radial conduction of water
37. Food materials can be stored in xylem parenchyma in all of these forms except –
(Pg. 87, E)
A) Starch B) Fat C) Tannin D) None
38. In stems, (Pg. 87, E)
A) Protoxylem lies towards centre and metaxylem towards periphery, called endarch
B) Protoxylem lies towards centre and metaxylem towards periphery, called exarch
C) Metaxylem lies towards centre and protoxylem towards periphery called endarch
D) Metaxylem lies towards centre and protoxylem towards periphery called exarch
39. In roots – (Pg. 87, E)
A) Protoxylem lies towards centre and metaxylem towards periphery, called endarch
B) Protoxylem lies towards centre and metaxylem towards periphery, called exarch
C) Metaxylem lies towards centre and protoxylem towards periphery called endarch
D) Metaxylem lies towards centre and protoxylem towards periphery called exarch
40. A maturāe sieve elements – (Pg. 88, E)
A) Have peripheral nucleus
B) Have peripheral cytoplasm and no nucleus
C) Have no vacuole and no nucleus
D) Have large vacuole and peripheral nucleus
41. Phloem fibres – (Pg. 88, E)
A) Are made of parenchyma B) Are made of collenchyma
C) Present in primary phloem D) Present in secondary phloem
42. Which of the statements about Phloem is correct? (Pg. 88, M)
A) Protoploem consists of narrow sieve tube
B) Metaphloem consists of narrow sieve tubes
C) Protopholem consists of bigger sieve tubes
D) Both protophloem and metaphloem have bigger sieve tubes.
Paragraph – 6.2
The tissue system
43. The three types of tissue systems – epidermal ground and vascular systems are classified based on their- (Pg. 88, E)
A) Function B) Location C) Structure D) Both (B) and (C)
Paragraph – 6.2.1
Epidermal tissue system
44. Outer layer of primary plant body is – (Pg. 88, E)
A) Epiblema B) Epidermis C) Epicarp D) Ectodermis
45. Waxy layer on epidermis- (Pg. 89, E)
A) is called trichome B) is called epiblema
C) is absent in roots D) help in exchange of gases
46. Consider the following statements – (Pg. 89, E)
i) Epidermal cells are parenchymatous.
ii) Epidermis is usually two – layered.
iii) Stomata are usually present in epidermis of stem.
iv) Outer walls of guard cells are thick and inner walls are thin.
v) Subsidiary cells are epidermal cells.
How many of these statements are incorrect?
A) 2 B) 1 C) 3 D) 4
47. Stomatal apparatus consists of – (Pg. 89, E)
A) Stomatal aperture only B) Stomatal aperture and guard cells
C) Subsidiary cells D) Both (B) and (C)
48. Epidermal cells modify to form (Pg. 89, E)
A) Trichomes only B) Trichomes, Root hairs, Stomata
C) Trichomes, Root hair, Subsidiary cells D) Root hairs only
49. Trichomes – (Pg. 89, E)
A) Present on stem and are multicellular
B) Present on root and are multicellular
C) Present on stem and are unicellular
D) Present on root and are unicellular
Paragraph – 6.2.2
The ground Tissue System
50. All tissues are included in ground tissue except – (Pg. 89, E)
A) Cortex B) Pith C) Pericycle D) Epidermis
51. In leaves, mesophyll is present in – (Pg. 89, E)
A) Epidermal tissue system B) Ground tissue system
C) Vascular tissue system D) Both (A) & (B)
Paragraph – 6.2.3
The Vascular Tissue System
52. In dicots stem, which condition is present (Pg. 90, E)
A) Cambium present between xylem & phloem, known as closed type vascular bundle
B) Cambium absent between xylem & phloem, known as closed type vascular bundle.
C) Cambium present outside xylem & phloem, known as open type vascular bundle
D) Cambium present between xylem & phloem, known as open type vascular bundle.
53. A : Monocot have closed type of vascular bundles
R : monocots do not show secondary growth (Pg. 90, H)
A) Both A and R are correct and R is correct explanation of A
B) Both A & R are correct and R is not the explanation of A
C) A is correct and R is incorrect
D) Both A & R are incorrect
54. Read given statements in context of given figure (Pg. 90, E)
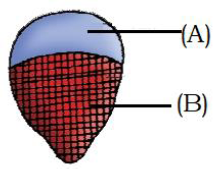
i) A is xylem and B is phloem
ii) A is phloem and B is xylem
iii) Primary xylem in figure is endarch type.
iv) Primary in figure is exarch type.
Choose the correct statements
A) (i) and (iii) B) (i) and (iv) C) (ii) and (iii) D) (ii) and (iv)
55. The given figure can be vascular bundle of (Pg. 90, E)
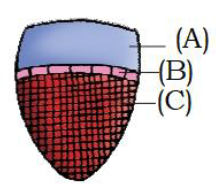
A) Shoot of sunflower B) Shoot of grass
C) Root of sunflower D) Root of grass
Paragraph – 6.3
Anatomy of Dicot & Monocot Plants
56. For understand the tissue organization of roots, stems and leaves better, it is convenient to study– (Pg. 90, E)
A) Longitudinal section of young and growing zones of organs
B) Transverse section of young & growing zones of organs
C) Longitudinal section of mature zones of organs
D) Transverse section of mature zones of organs
Paragraph – 6.3.1
Dicotyledonous Root
57. Choose correct order of cells from outside to inside in a sunflower root- (Pg. 90, E)
A) Epidermis – endodermis – cortex – pericycle
B) Epiblema – cortex – endodermis – pericycle
C) Epiblema – cortex – pericycle – endodermis
D) Epidermis – endodermis – pericycle – cortex
58. Suberin is deposited on – (Pg. 90, E)
A) Tangential walls of epidermal cells
B) Radial walls of cortical cells
C) Tangential walls of endodermal cells
D) radial walls of epidermal cells
59. The substance that casparian strips is made up of is – (Pg. 91, E)
A) waxy B) water – impermeable
C) suberin D) all of these
60. Initiation of lateral roots in dicot during secondary growth occurs in – (Pg. 91, E)
A) Endodermal cells B) Pericycle
C) Medullary ray D) Conjunctive tissue
61. Initiation of vascular cambium in dicot root during secondary growth occurs from –
(Pg. 91, E)
A) Thin walled parenchymatous cells
B) Thick walled collenchyma cells
C) Thinn walled endodermal cells
D) Thick walled parenchyma cells
62. Which of the following is true about
A) Parenchymatous and lie outside phloem
B) Parenchymatous and lie outside endodermis
C) Collenchymatous and lie between xylem and phloem
D) Parenchymatous and lie between xylem & phloem
63. Endodermis is present in dicot root in (Pg. 91, E)
A) Two layer with little intercellular spaces
B) Two layer without any intercellular spaces
C) Single layer with little intercellular spaces
D) Single layer without any intercellular spaces
64. Cortex of dicot root consists of – (Pg. 91, E)
A) Multi layers of thick walled parenchyma
B) Multi layers of thin walled parenchyma
C) Single layer of thick walled parenchyma
D) Single layer of thin walled parenchyma
65. Innermost layer of cortex in dicot root is – (Pg. 91, E)
A) Pericycle B) Hypodermis C) Endodermis D) Pith
66. Parenchyma cells are generally thin walled. An example of thick-walled parenchyma in dicot root is (Pg. 91, E)
A) Pith B) Pericycle C) Endodermis D) Hypodermis
67. Stele includes (Pg. 91, E)
A) Endodermis, pericycle, pith
B) Endodermis, pericycle, vascular bundles
C) Pericycle, vascular bundle, pith
D) Endodermis, vascular bundle, pith
68. Identify the figure (i) & (ii) (Pg. 91, E)
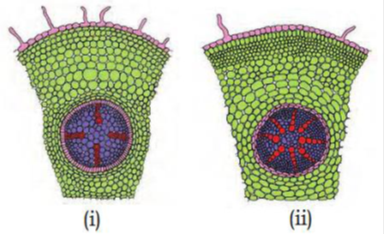
A) (i)– T.S of dicot root (ii) – T.S of monocot root
B) (i) – T.S of dicot stem (ii) – T.S of monocot stem
C) (i) – T.S of monocot root (ii) – T.S of dicot root
D) (i) – L.S of monocot stem (ii) – L.S of dicot root
69. Identify the correct labels of monocot root T.S (Pg. 91, E)
A) (i)- cortex, (ii)- endodermis, (iii)- pericycle
B) (ii)- cortex, (i)- endodermis, (iii)- pericycle
C) (iii)- cortex, (ii)- endodermis, (i)- pericycle
D) (i)- cortex, (iii)- endodermis, (ii)- pericycle
Paragraph – 6.3.2
Monocotyledonous Root
70. Xylem bundles in monocot root- (Pg. 91, E)
A) Are fewer than dicot root B) Are less than six
C) Are polyarchy D) All of the above
71. Secondary growth in monocot roots occur- (Pg. 91, E)
A) By vascular cambium B) By interfascicular cambium
C) Both A & B D) None of these
Paragraph – 6.3.3
Dicotyledonous Stem
72. Epidermis of dicot stem- (Pg. 91, E)
A) Is called epiblema B) Lacks stomata
C) Has a thin layer of cuticle D) Lacks trichomes
73. Cortex in dicot stem is found between- (Pg. 92, E)
A) Epidermis and endodermis B) Endodermis and pericycle
C) Pericycle and pith D) Endodermis and pith
74. Hypodermis of dicot stem is made of- (Pg. 92, E)
A) Parenchyma B) Collenchyma
C) Sclerenchyma D) All of these
75. Starch sheath is found in dicot stem in- – (Pg. 92, E)
A) Endodermis B) Cortex C) Pericycle D) Pith
76. Cortical cells dicot stem has- (Pg. 92, E)
A) No intercellular spaces
B) Inconspicuous intercellular spaces
C) Conspicuous intercellular spaces
D) Very large intercellular spaces
77. Pericycle of dicot stem is present in the form of- (Pg. 92, E)
A) Semi – square patches of collenchyma
B) Semi – lunar patches of sclerenchyma
C) Semi – lunar patches of collenchyma
D) Semi – lunar patches of parenchyma
78. Medullary rays are – (Pg. 92, E)
A) Axially placed, parenchymatous
B) Axially placed, collenchymatous
C) Radially placed, parenchymatous
D) Radially placed, collenchymatous
79. Location of medullary rays – (Pg. 92, E)
A) Above endodermis
B) Between endodermis and pericycle
C) Between pericycle and cortex
D) Between vascular bundles
80. In sunflower stem, vascular bundle is- (Pg. 93 E)
A) Conjoint, closed, exarch protoxylem
B) radial, open, endarch protoxylem
C) conjoint, open, exarch protoxylem
D) conjoint, open, endarch protoxylem
81. which of these is incorrect about pith of dicot stem? (Pg. 93, E)
A) Parenchymatous cells B) No intercellular space
C) Central portion of stem D) Large intercellular space
82. Identify the correct labels (Pg. 92, E)
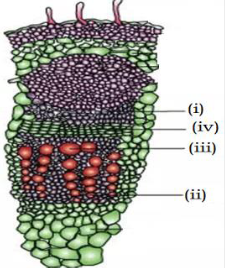
A) (i)- protoxylem, (ii)- cambium, (iii)-phloem, (iv)- metaxylem
B) (ii)- protoxylem, (iv)- cambium, (i)-phloem, (iii)- metaxylem
C) (iv)- protoxylem, (i)- cambium, (ii)- phloem, (iii)- metaxylem
D) (iii)- protoxylem, (iv)- cambium, (i)- phloem, (ii)- metaxylem
83. Identify endodermis in the given figure- (Pg. 92, E)
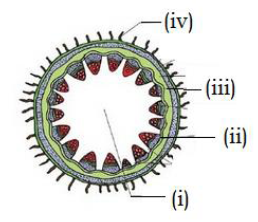
A) (i) B) (ii) C) (iv) D) (iii)
Paragraph – 6.3.4
Monocot Stem
84. Select the correct match of columns A & B (Pg. 93, M)
Column A Column B
i Hypodermis of grasses stem 1) parenchyma
ii Hypodermis of sunflower stem 2) Collenchyma
iii Bundle sheath of grasses stem 3) Sclerenchyma
iv Ground tissue of grasses stem
A) (i)- 2, (ii)- 3 B) (iv)- 1, (iii)- 1 C) (iii)- 3, (i)- 3 D) (ii)- 1, (iv)- 3
85. In monocot stem, (Pg. 93, E)
A) Peripheral vascular bundles are generally smaller than central ones
B) Central vascular bundles are generally smaller than peripheral ones
C) Both peripheral and central are almost same sized
D) None of these
86. Phloem parenchyma is absent in- (Pg. 93, E)
A) Gymnosperms B) Monocots C) Both D) None
87. The given figure is (Pg. 92, E)

A) Monocot root B) Dicot root C) Monocot stem D) Dicot stem
Paragraph – 6.3.5
Dorsiventral leaf (Dicot)
88. Read the given statements and choose the number of correct statements (Pg. 93, M)
(i) Leaf of dicot lack cuticle
(ii) Stomata on adaxial side of epidermis is more in number than abaxial side
(iii) Mesophyll is the ground tissue in dicot leaf
(iv) The adaxial epidermis may lack stomata
A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4
89. In the leaf of sunflower, mesophyll lies- (Pg. 93, E)
A) Between epidermis and cortex
B) Between adaxial epidermis and abaxial epidermis
C) Between endodermis and pericycle
D) Between pericycle and vascular bundles
90. Which of the given statements about dicot leaf is incorrect? (Pg. 93, M)
A) The abaxial palisade parenchyma is made of elongated cells
B) Spongy parenchyma is oval or round
C) The spongy parenchyma has large spaces between cells
D) The parenchyma on adaxial side of leaf are arranged vertically & parallel to each other
91. Consider the statements given below- (Pg. 93, M)
a) Size of vascular bundle in leaf depend upon size veins
b) Vascular bundles in leaf are surrounded by bundle sheath cells
A) (a) is correct & (b) is incorrect B) (a) is incorrect & (b) is correct
C) Both are correct D) Both ate incorrect
92. Identify the correct option in context of given figures (Pg. 93, E)
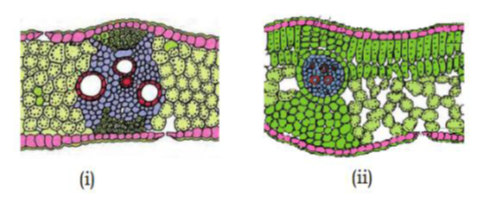
A) (i)- dicot stem, (ii)- monocot stem
B) (i)- dicot leaf, (ii)- monocot leaf
C) (i)- monocot stem, (ii)- dicot stem
D) (i)- monocot leaf, (ii)- dicot leaf
Paragraph – 6.3.6
Isobilateral Leaf (Monocot)
93. Which of the following is correct for isobilateral leaves? (Pg. 94, E)
A) Present in all angiosperms
B) Two different types of mesophyll are found
C) Stomata on both surfaces of mesophyll
D) Has similar sizes of vascular bundles
94. In grasses, large, empty, colourless cells are called- (Pg. 94, E)
A) Subsidiary cells B) Complementary cells
C) Cortical cells D) None of these
95. Identify the incorrect statement in regards to bulliform cells- (Pg. 94, E)
A) Present on abaxial side B) Empty cells
C) Makes leaf curl inward when flaccid
D) Helps to minimize water loss
96. Identify correct labels for given figure. (Pg. 94, E)
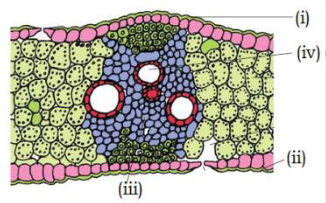
A) (i)- adaxial epidermis (ii)- abaxial epidermis, (iii)- xylem (iv)- phloem
B) (ii)- adaxial epidermis (i)- abaxial epidermis, (iii)- xylem (iv)- phloem
C) (i)- adaxial epidermis (ii)- abaxial epidermis, (iv)- xylem (iii)- phloem
D) (ii)- adaxial epidermis (i)- abaxial epidermis, (iv)- xylem (iii)- phloem
Paragraph – 6.4
Secondary growth
97. Increase in girth of plant- (Pg. 94, E)
A) Involves lateral meristem B) Involves intercalary meristem
C) Involves apical meristem D) All of these
Paragraph – 6.4.1
Vascular Cambium
98. Vascular cambium- (Pg. 94, E)
i) Is meristematic
ii) Present in patches between xylem and phloem in young stem
iii) Present as a single layer between xylem and phloem in young stem
iv) Forms complete ring later How many of the above statements are correct-
A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4
Paragraph – 6.4.1.1
Formation of cambial ring
99. In dicot stem, cambium cells present between xylem & phloem is- (Pg. 94, E)
A) Intrafasicular cambium B) Interfascicular cambium
C) Cork cambium D) Cortical cambium
100. Interfasicular cambium is formed by- (Pg. 94, E)
A) Pericycle cells B) Endodermal cells
C) Medullary cells D) Complementary cells
Paragraph – 6.4.1.2
Activity of Cambial Ring
101. Cambial ring cuts off new cells- (Pg. 95, E)
A) Towards inner side only B) Towards outer side only
C) Towards inner and outer side both D) Along its own axis
102. Cambial ring cuts off new cells – (Pg. 95, E)
A) Towards pith, called secondary phloem
B) Towards pith, called secondary cambium
C) Towards pith, called secondary medullary rays
D) Towards pith, called secondary xylem
103. Cambial ring cut off – (Pg. 95, E)
A) More cells on outer side B) More cells on inner side
C) Equal cells on both sides D) Cells randomly
104. Assertion: secondary xylem form a compact mass.
Reason: cambium is lesser active on outer side comparatively.
Choose the best option- (Pg. 95, H)
A) Assertion & Reason both are correct and Reason is correct explanation for
Assertion.
B) Assertion & Reason both are correct and Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion
C) Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect
D) Assertion is incorrect but Reason is correct
105. Secondary medullary rays are- (Pg. 95, E)
A) Narrow bands of parenchyma
B) Narrow bands of meristem
C) Wide bands of parenchyma
D) Wide bands of meristem
106. Which of these is correct about activity of cambial ring? (Pg. 95, E)
A) Secondary xylem crushes primary xylem
B) Secondary xylem crushes primary phloem
C) Secondary xylem crushes secondary phloem
D) Both B & C
107. Identify the secondary xylem in the figure- (Pg. 95, E)
A) (i) B) (ii) C) (iii) D) (iv)
Paragraph – 6.4.1.3
Spring wood and autumn wood
108. Activity of cambium is under control of- (Pg. 96, E)
A) Physiological factors B) Environmental factors
C) Both A & B D) Depend on season only
109. In spring, cambium produce (Pg. 96, E)
A) Less xylary elements, having vessels with wider cavities
B) More xylary elements, having vessels with wider cavities
C) Less xylary elements, having vessels with narrow cavities
D) More xylary elements, having vessels with narrow cavities
110. Select the characters of autumn wood from the list- (Pg. 96, E)
i) Light in colour ii) Dark in colour
iii) Low density iv) High density
v) Wider vessels vi) Narrow vessels
A) i, iii, v B) i, iv, vi C) ii, iv, vi D) ii, iii, v
111. Annual rings are constituted by- (Pg. 96, E)
A) Alternate concentric rings of 3 types of woods
B) continuous concentric rings of 3 types of woods
C) Alternate concentric rings of 2 types of woods
D) continuous concentric rings of 2 types of woods.
Paragraph – 6.4.1.4
Heartwood & Sapwood
112. Heartwood is- (Pg. 96, E)
A) Light in colour B) Dark in colour
C) Alternately light & dark in colour D) None of these
113. Consider the following statements about heartwood- (Pg. 96, E)
i) Lighter in colour
ii) Comprises dead elements
iii) Suberized walls
iv) Resistant to attack of micro-organisms
v) Conducts water and provide mechanical support to plant
How many of the statements are correct?
A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 5
Paragraph – 6.4.2
Cork Cambium
114. Assertion: Cork cambium is needed due to activity of vascular cambium
Reason: Phellogen is present below endodermis
Select the appropriate answer- (Pg. 96, E)
A) Both Assertion & Reason are correct
B) Assertion is correct and Reason is wrong
C) Assertion is wrong and Reason is correct
D) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong
115. Phellogen is made of- (Pg. 96, E)
A) Narrow, thick-walled, meristematic cells
B) Narrow, thin-walled, parenchyma
C) Narrow, thick-walled, parenchyma
D) Narrow, thin-walled, meristem
116. Phellogens cuts- (Pg. 96, E)
A) Cork on inner side and phelloderm on outside
B) Phellem on inner and secondary cortex on outside
C) Bark on outside and secondary cortex on inside
D) Phellem on outside and phelloderm on inside
117. Cork is impervious to water due to (Pg. 96, E)
A) Lignin B) Suberin C) Keratin D) Cellulose
118. Bark includes – (Pg. 97, E)
A) Secondary xylem and periderm
B) Secondary phloem and periderm
C) Pericycle and vascular cambium
D) Pith and stele
119. Phlloderm is – (Pg. 97, E)
A) Parenchymatous B) Collenchymatous
C) Sclerenchymatous D) Meristematic
120. Lenticles are (Pg. 97, E)
A) Circle – shaped B) Rectangular
C) Lens – shaped D) Polygonal shaped
121. Select the correct labels – (Pg. 97, E)
A) (i) – complimentary cells B) (ii) – cork cambium
C) (iii) – secondary cortex D) (iv) – epidermis
Paragraph – 6.4.3
Secondary Growth in Roots
122. In sunflower root. Vascular cambium is originated from tissues – (Pg. 97, E)
A) Below phloem bundle B) Of pericycle
C) Of interfascicular cambium D) Both (A) & (B)
123. Secondary growth does not occur in – (Pg. 98, E)
A) Gymnosperm stem B) Gymnosperm root
C) Monocot D) All of these
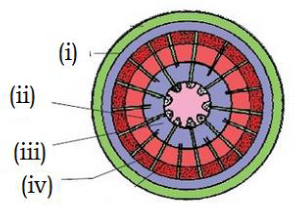
124. Identify the cambial ring – (Pg. 98, E)
A) (i) B) (iii) C) (iv) D) (ii)
ANSWERS
| 1) D | 2) C | 3) C | 4) D | 5) A | 6) C | 7) D | 8) C | 9) A | 10) C |
| 11) D | 12) C | 13) D | 14) B | 15) C | 16) B | 17) D | 18) D | 19) C | 20) D |
| 21) D | 22) A | 23) D | 24) C | 25) A | 26) D | 27) B | 28) A | 29) A | 30) B |
| 31) B | 32) D | 33) A | 34) A | 35) A | 36) D | 37) D | 38) A | 39) D | 40) B |
| 41) D | 42) A | 43) D | 44) B | 45) C | 46) C | 47) D | 48) C | 49) A | 50) D |
| 51) B | 52) D | 53) B | 54) C | 55) A | 56) D | 57) B | 58) C | 59) D | 60) B |
| 61) D | 62) D | 63) D | 64) B | 65) C | 66) B | 67) C | 68) C | 69) B | 70) C |
| 71) D | 72) C | 73) A | 74) B | 75) A | 76) C | 77) B | 78) C | 79) D | 80) D |
| 81) B | 82) B | 83) D | 84) C | 85) A | 86) B | 87) C | 88) B | 89) B | 90) A |
| 91) C | 92) D | 93) D | 94) D | 95) A | 96) C | 97) A | 98) D | 99) A | 100) C |
| 101) C | 102) D | 103) B | 104) A | 105) A | 106) D | 107) C | 108) C | 109) B | 110) C |
| 111) C | 112) B | 113) A | 114) B | 115) D | 116) D | 117) B | 118) B | 119) A | 120) C |
| 121) B | 122) D | 123) C | 124) B | ||||||
